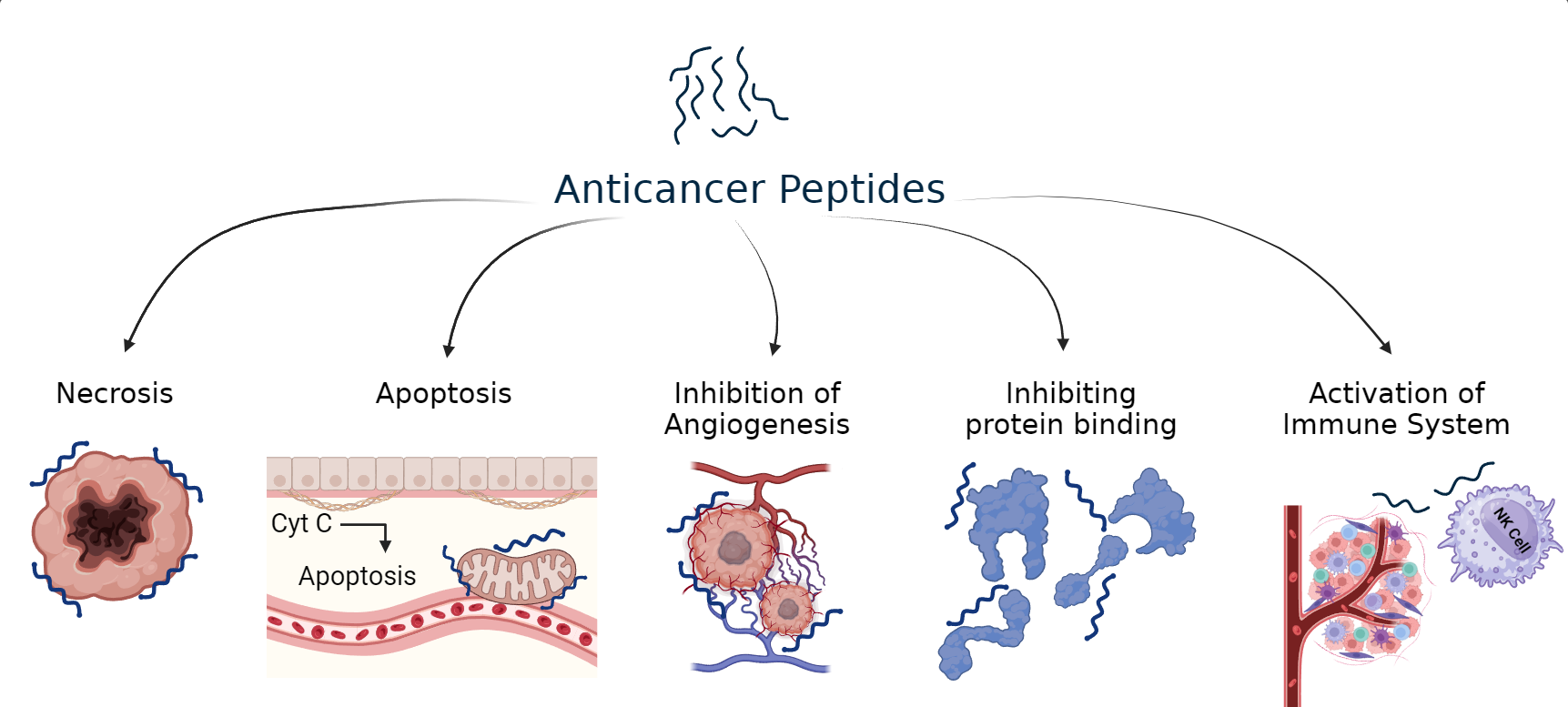
About ACPs
Anticancer Peptides (ACPs) are a class of short peptides that can inhibit tumor cell proliferation. Some properties of ACPs such as high selectivity, high penetration and easy modifications make them a superior choice for therapeutics as compared antibodies and small molecules.
Search
This section provides information about how to perform searches.
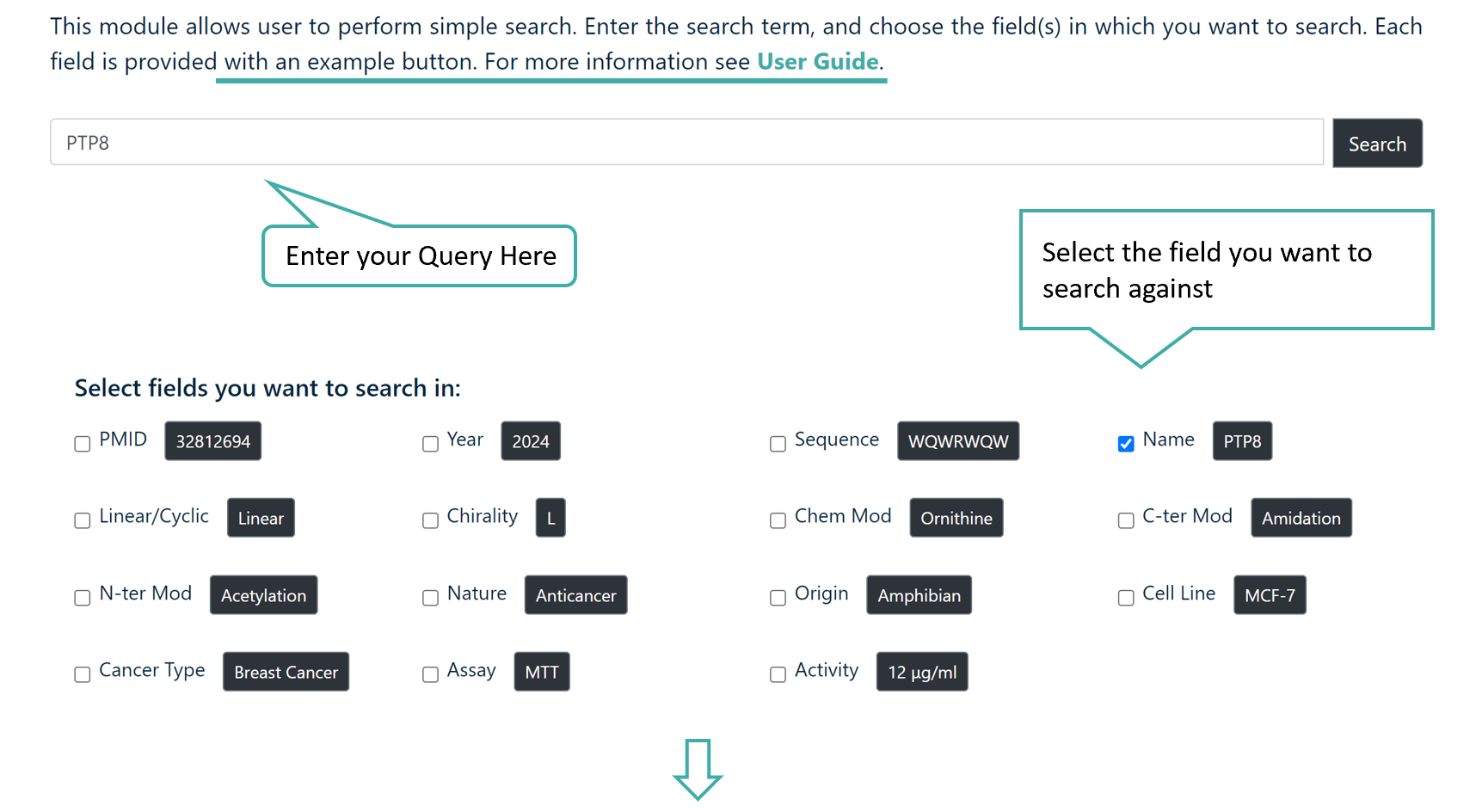
Basic Search
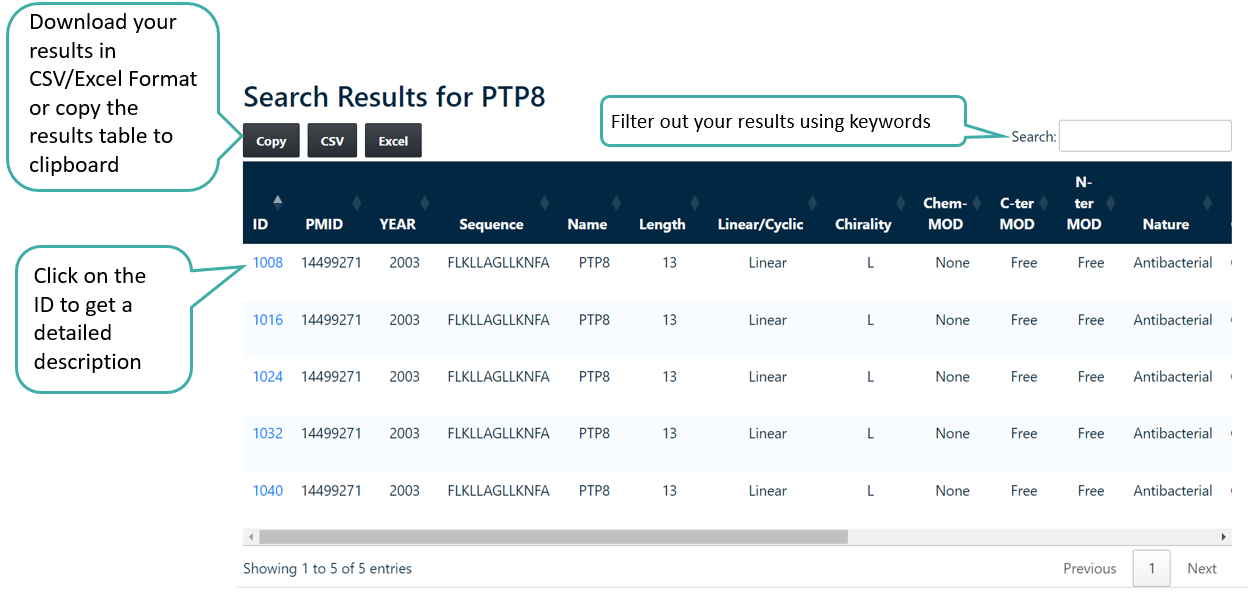
The user can input a search term in the search field and select the checkboxes to choose the specific fields they want to search.
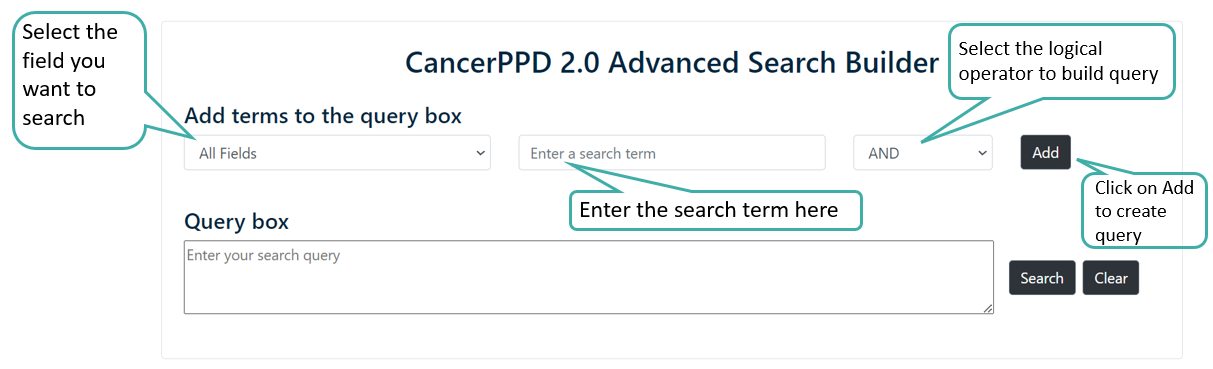
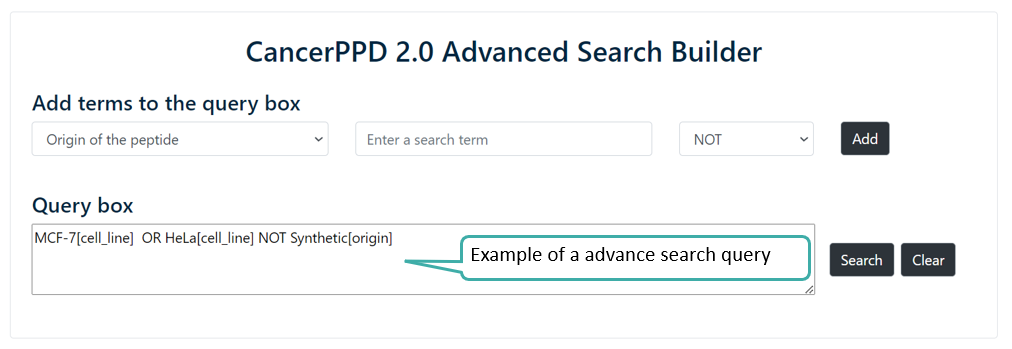
Advance Search
Users can perform advance search by selecting multiple fields using logical operators like AND/OR. Users can build the query by using the "Add" button.
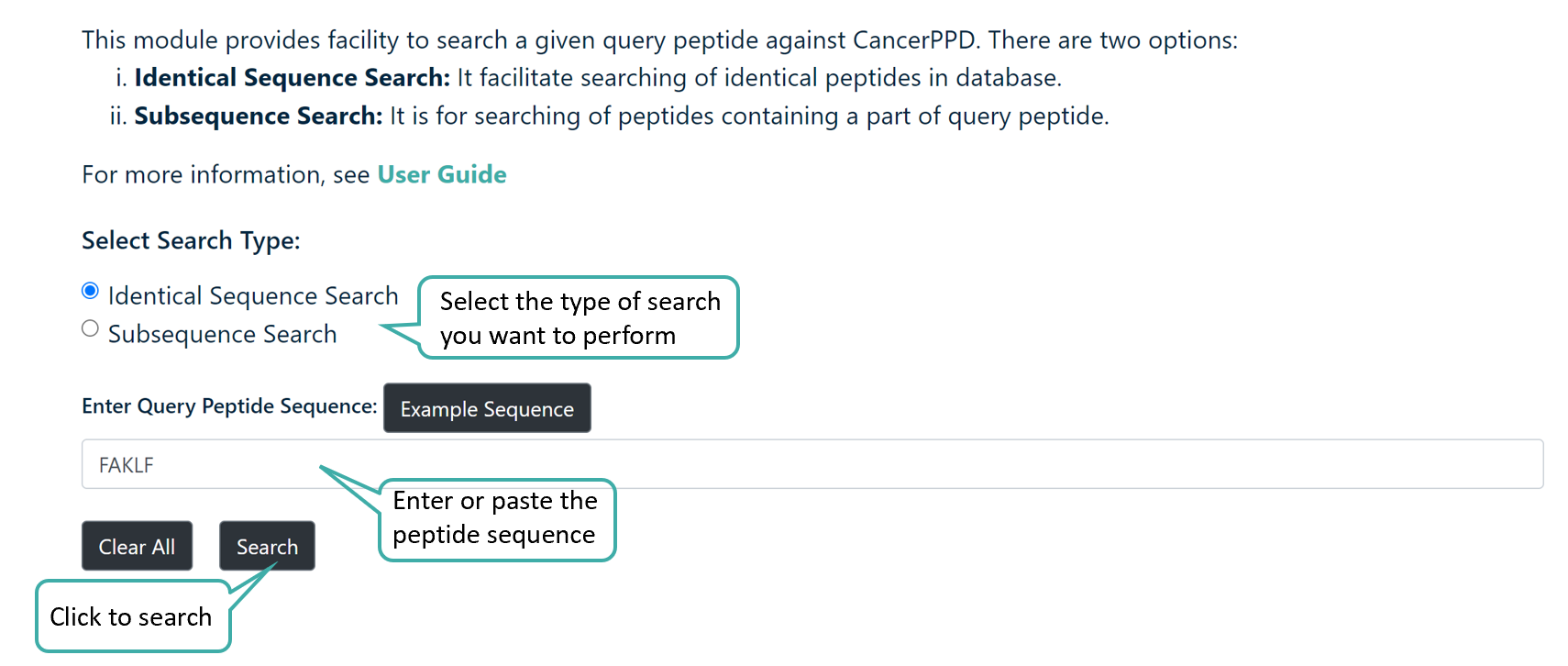
Peptide Search
Users can perform Peptide search to search for their query peptide sequence in the CancerPPD 2.0 Database. The module provides two search options:
- Identical Sequence Search: This option will search for identical peptide sequence in the database.
- Subsequence Search: This option will will search for peptides that contains a part of the query peptide.
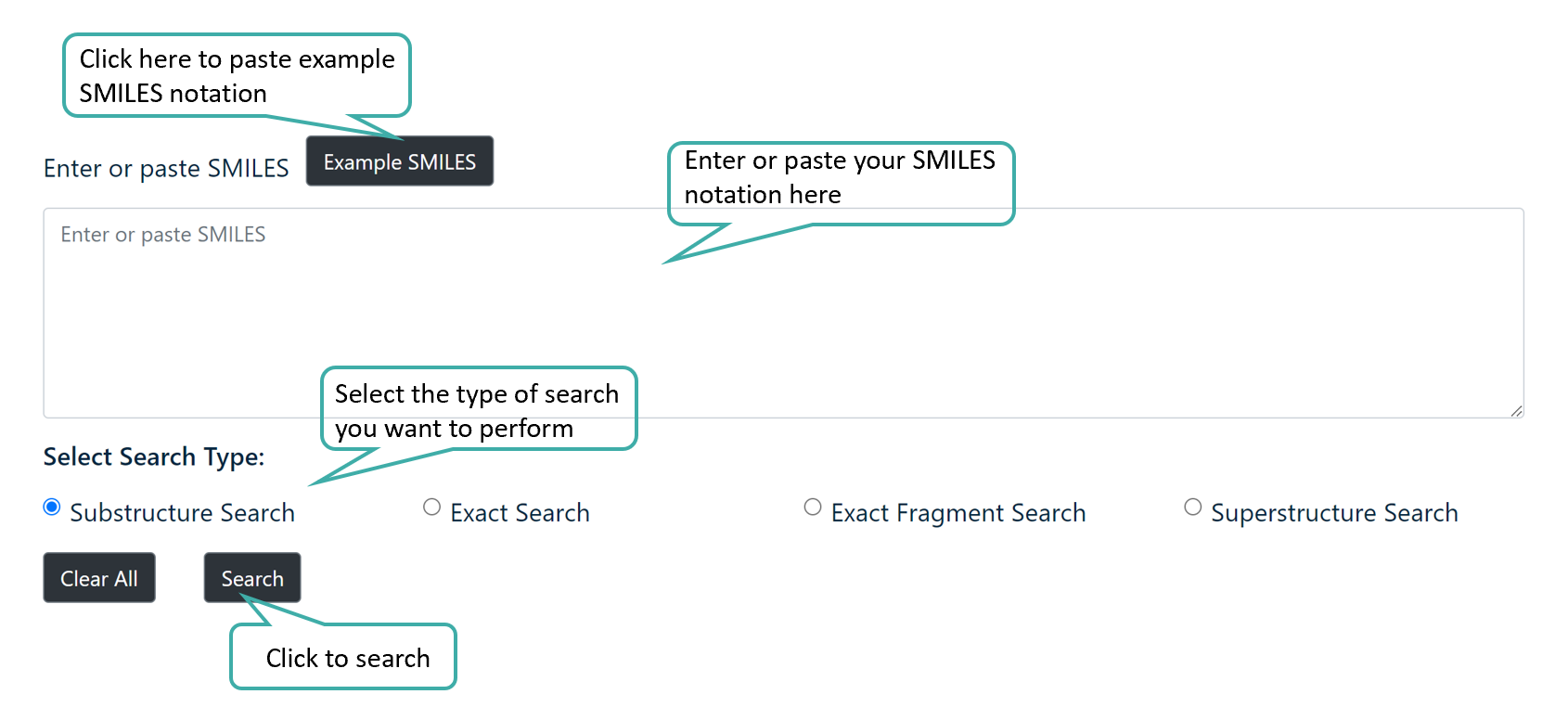
SMILES Search
Users can perform SMILES search to search for the query SMILES sequence in the CancerPPD 2.0 Database. The module provides four search options:
- Substructure Search
- Exact Search
- Exact Fragment Search
- Superstructure Search
Browse
This section provides information about browsing the CancerPPD 2.0 entries by different ways.
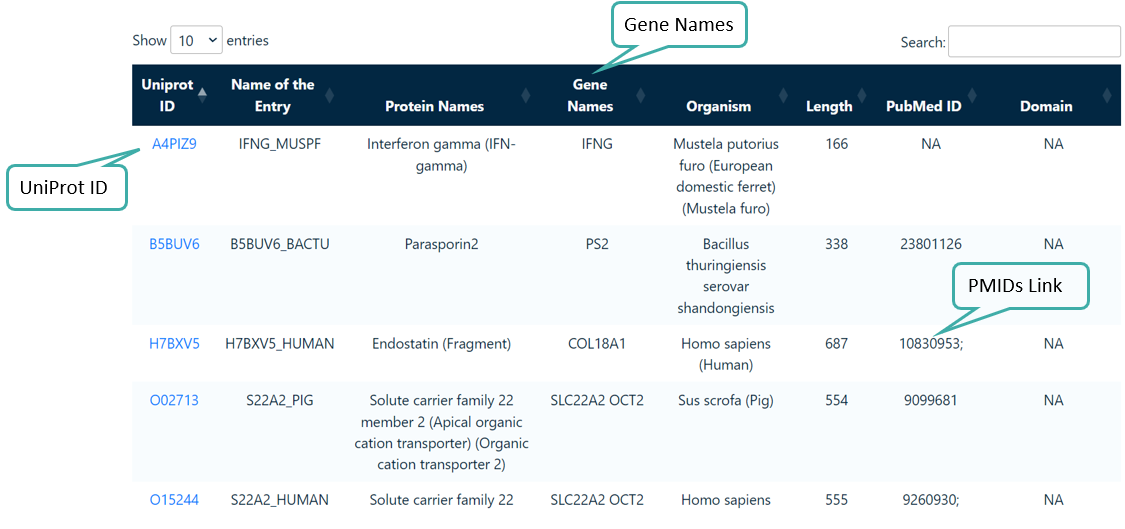
Browse by UniProt Proteins
Users can browse anticancer proteins mapped from UniProt.
Browse by Proteins
Users can browse anticancer proteins. The sequences with length greater than 40 were treated as proteins.
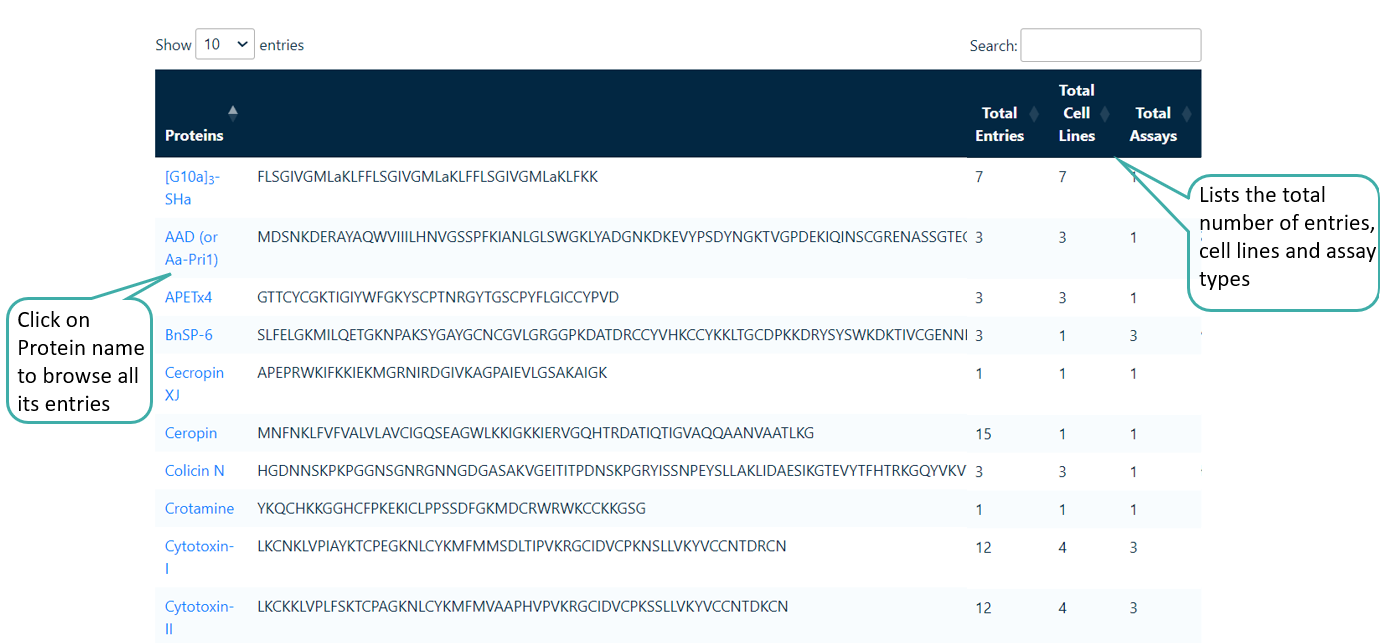
Browse by Peptide
Users can browse the unique anticancer peptides. It lists the number of entries for each peptide, the number of types of tissues effected, number of cell lines on which it has been tested and the number of different types of assays used to test each peptide.
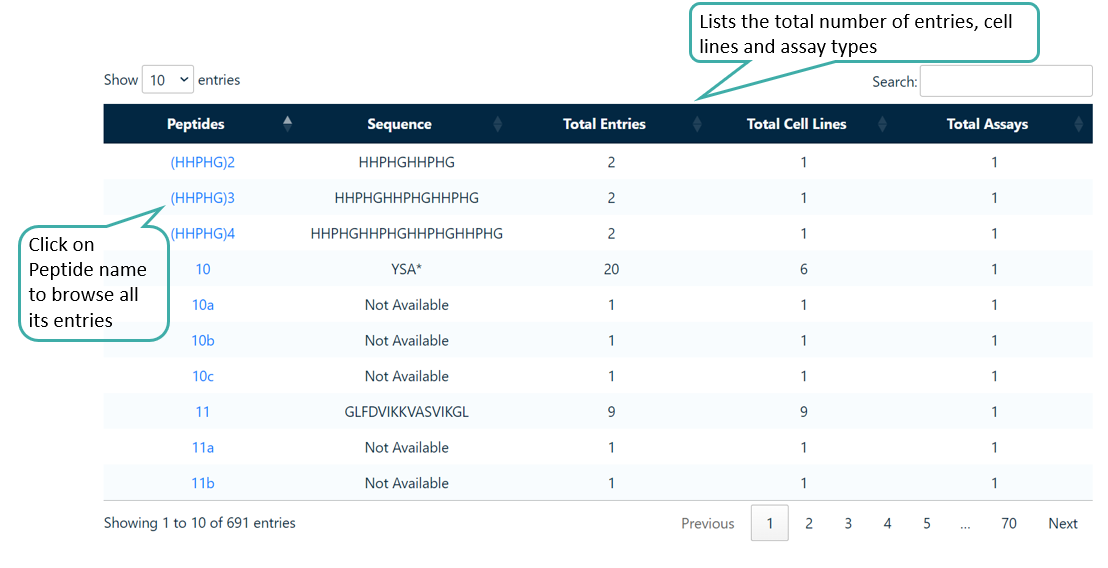
Browse by Tissue
Users can browse the tissue types against which anticancer peptides have been tested. It lists the number of entries, number of unique peptides and the number of cell lines tested for a particular tissue type.
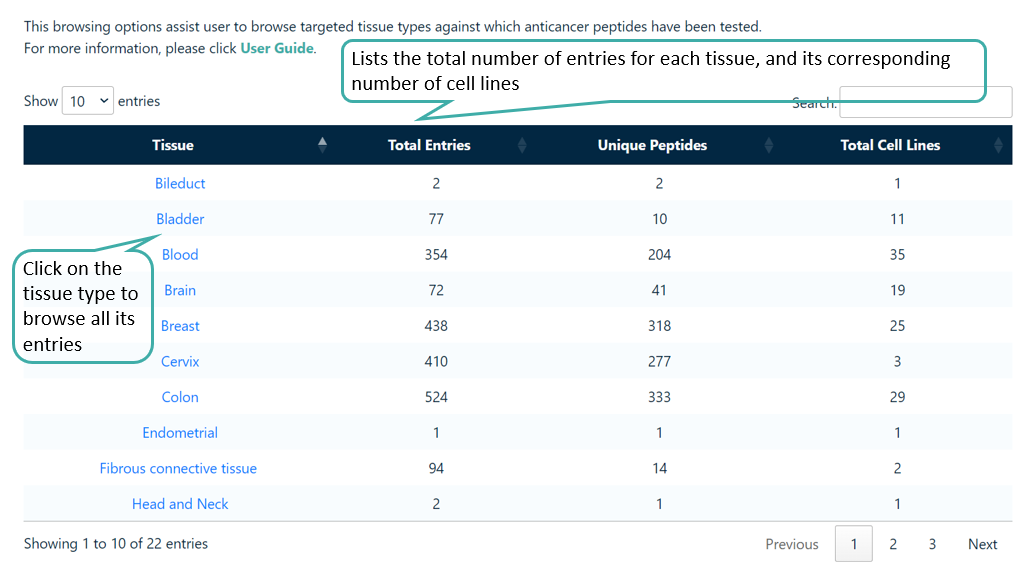
Browse by Cell Lines
Users can browse the the listed cell lines against which anticancer peptides have been tested. It also lists the total number of entries in CancerPPD 2.0 for each cell line.
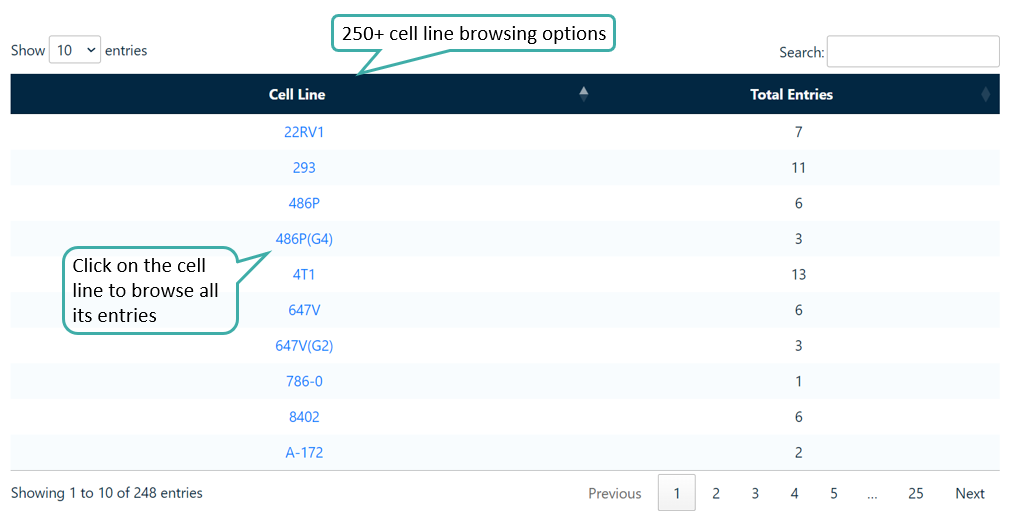
Browse by Year of Publication
Users can browse the the listed cell lines against which anticancer peptides have been tested. It also lists the total number of entries in CancerPPD 2.0 for each cell line.

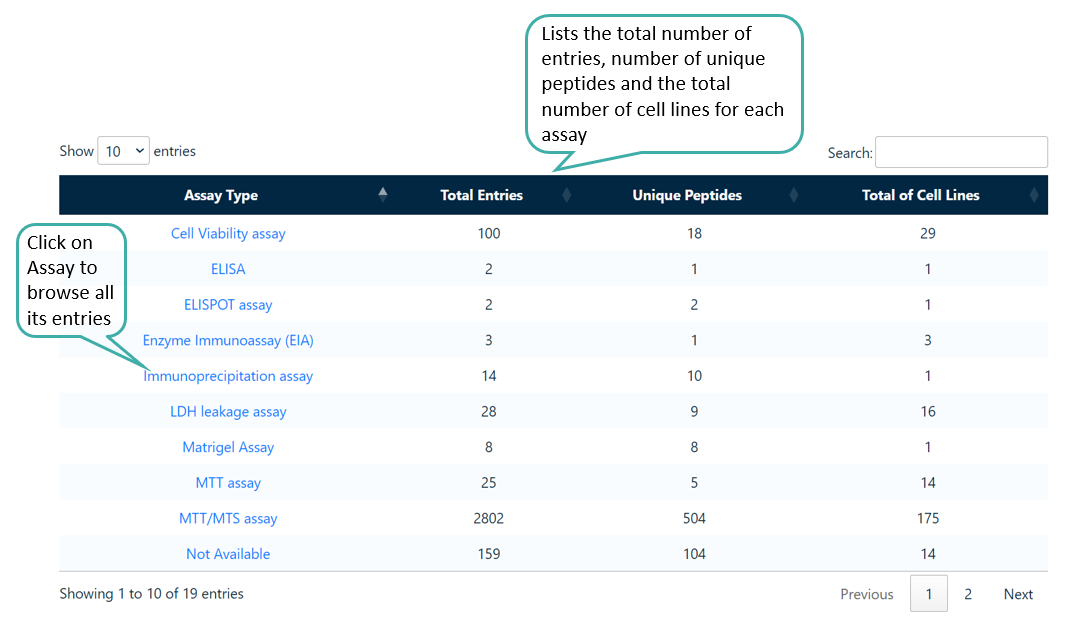
Browse by Assay
Users can browse the the listed assays using which anticancer peptides have been tested. It also lists the total number of entries, number of unique peptides and the total number of cell lines.
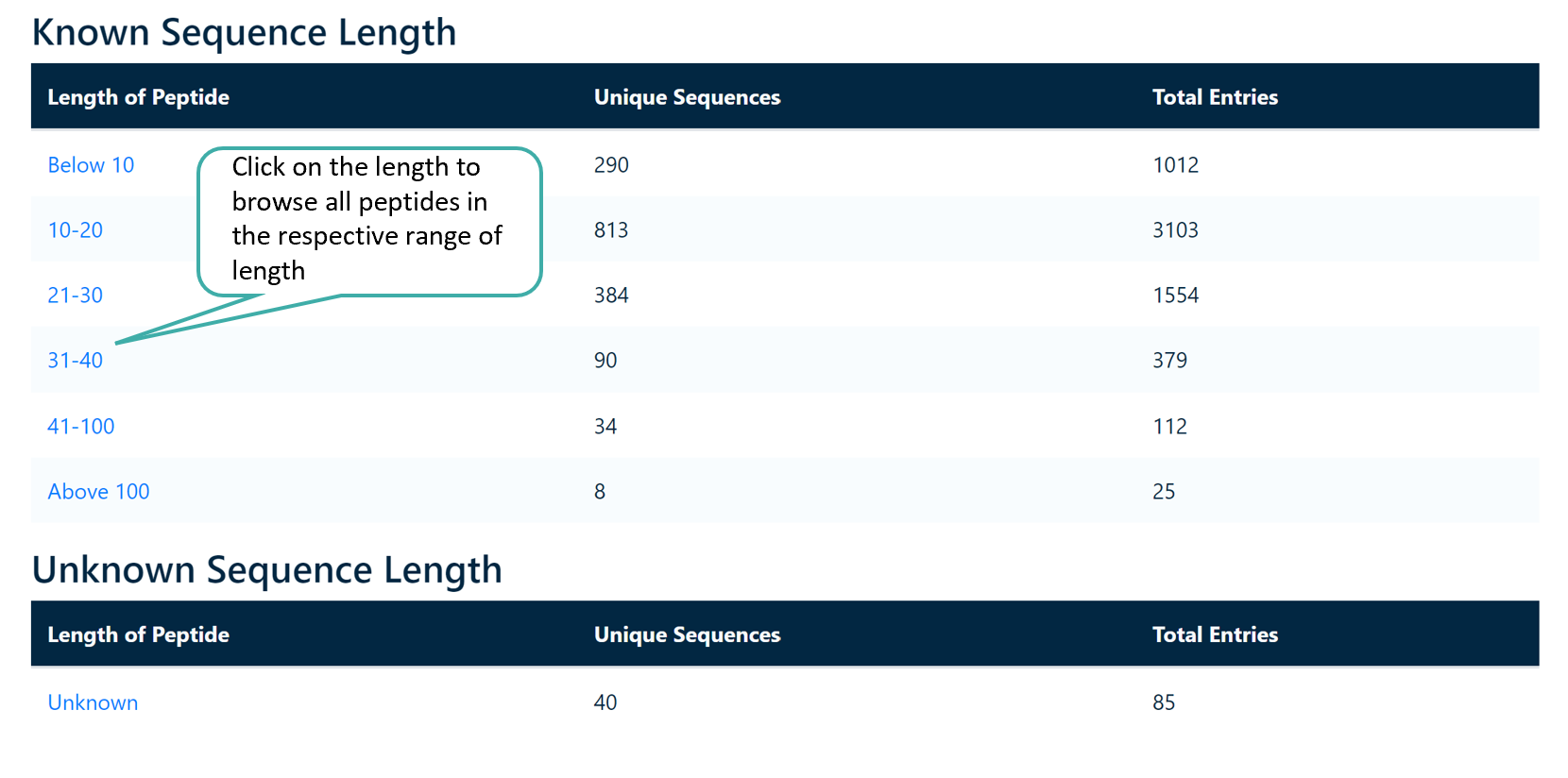
Browse by Length
Users can browse anticancer peptides in CancerPPD 2.0 based on their length. Sequences up to 40 amino acids are classified as peptides, while those exceeding 40 amino acids are classified as proteins.
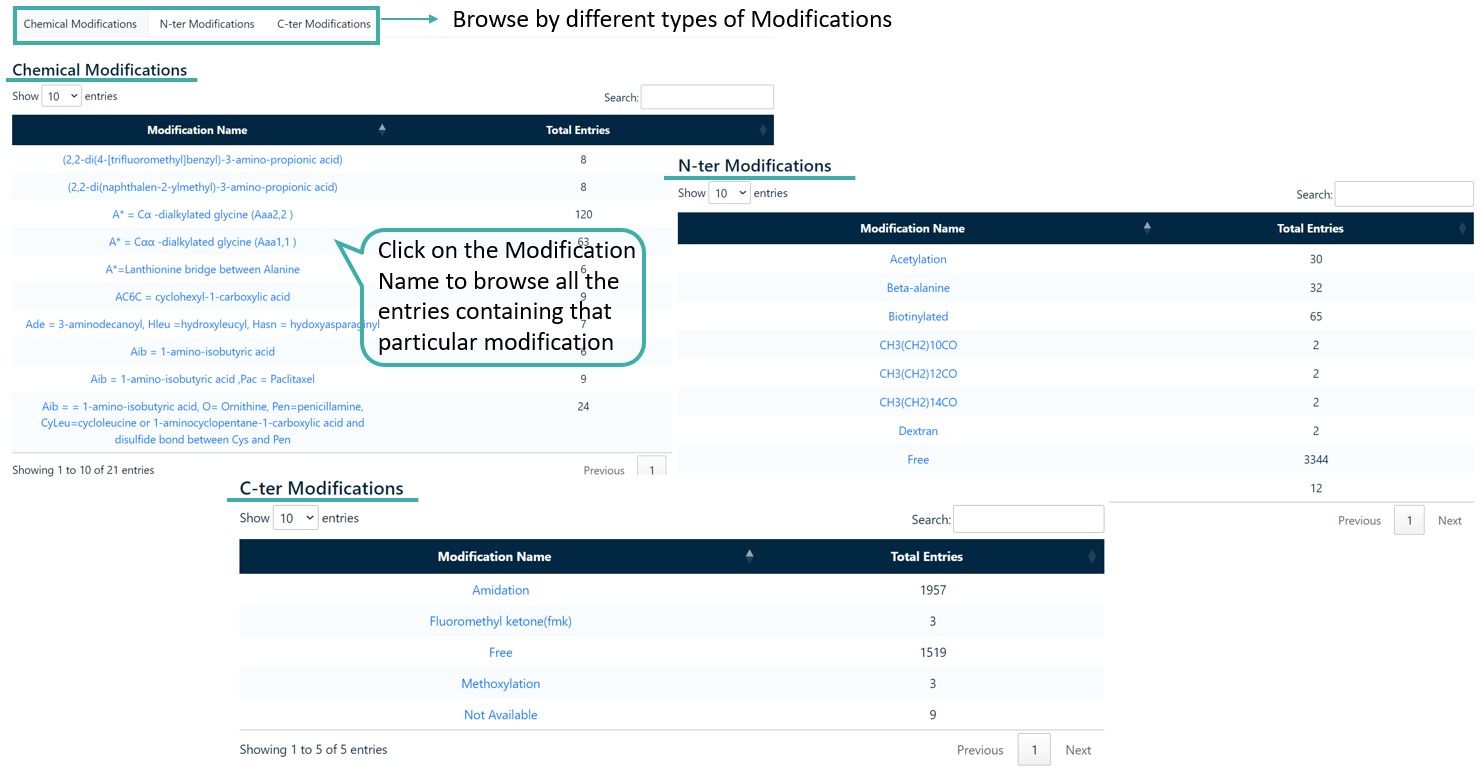
Browse by Modifications
Users can browse various C-terminal modifications, N-terminal modifications as well as the chemical modifications that were incorporated in the anticancer peptides compiled in CancerPPD 2.0.
Peptide Card
The peptide card contains all the information about a given peptide or protein. The peptide card contains the Basic Information such as PMID, origin, Sequence, Length etc., Information about Modifications such as Chemical Modifications, C-Ter Modifications, N-Ter Modifications, Experimental Data such as Activity, Assay, Cell Line etc., Literature Information such as Title of the paper, DOI, Journal, Abstract etc., Secondary Infromation (DSSP and SMILES) and External Links to PDB, SwissProt or TrEMBL.
The peptide and protein structures present in CancerPPD 2.0 includes both structures from PDB (experimental) and Predicted Structures. The structures also contains some associated data.
- DSSP States
- SMILES
Peptide Card of a Entry in CancerPPD 2.0
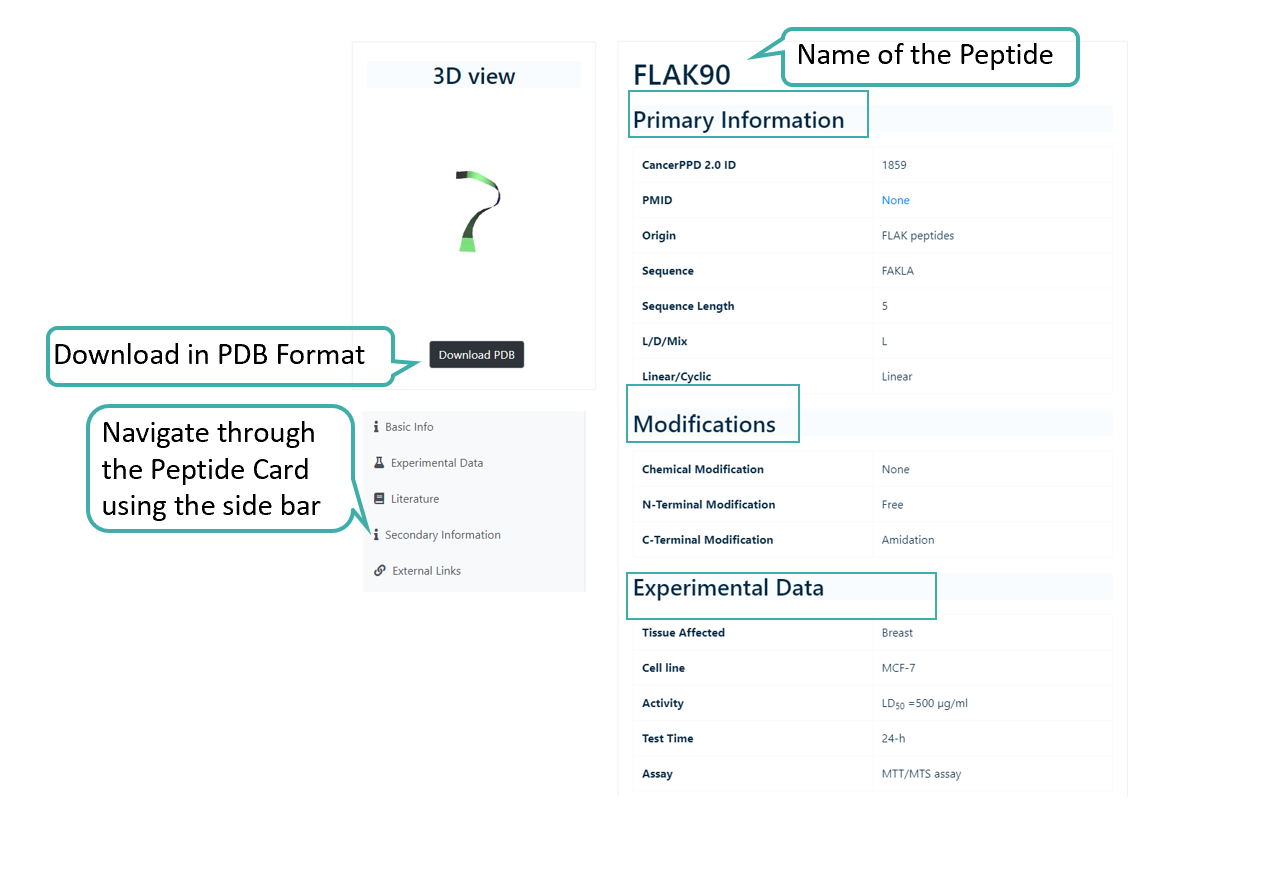
3D Structure
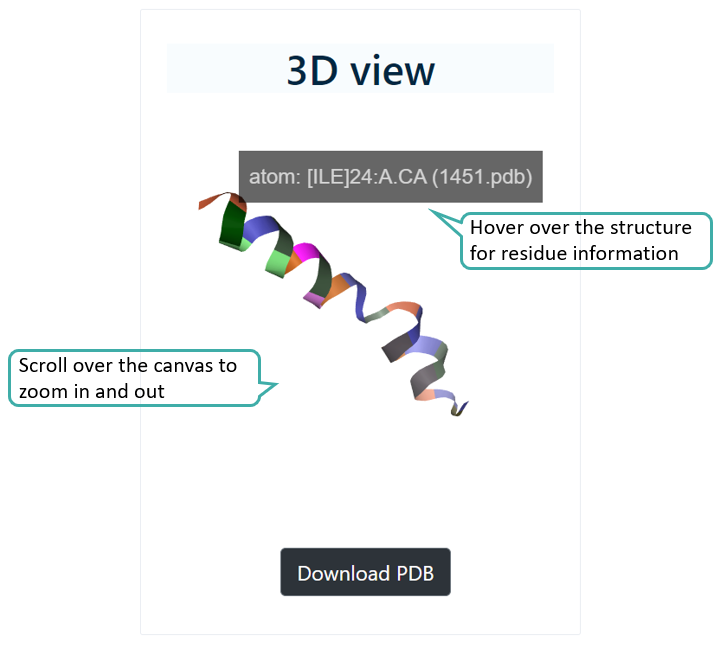
Tools
This section provides information about the tools available in CancerPPD 2.0.
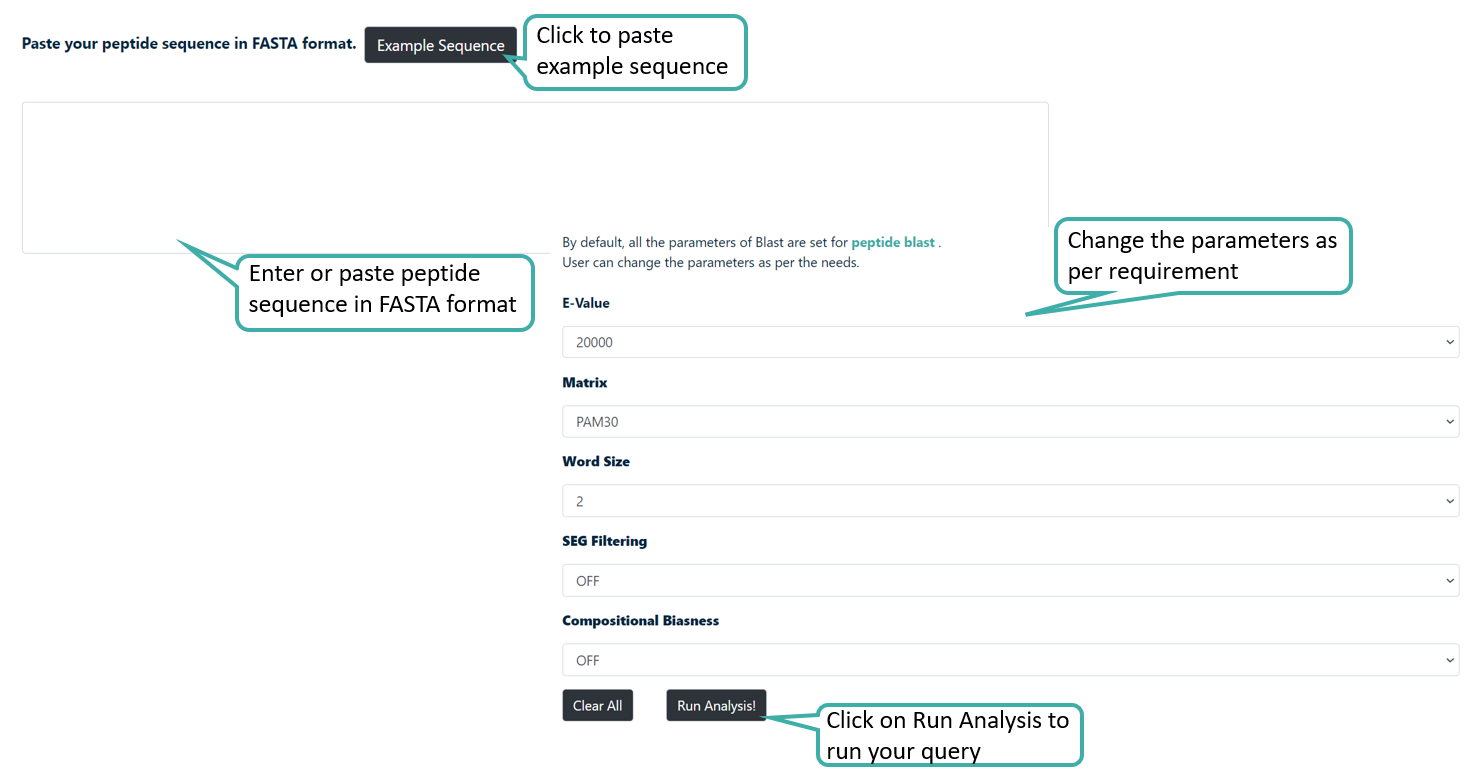
BLAST
Users can run a BLAST query against the CancerPPD 2.0 database. After submission of job it returns the list of peptides similar to the query peptide. The server also provides options to choose different parameters like weight matrix and expectation value.
Smith-Waterman Search
Users can run a Smith-Waterman search query against the CancerPPD 2.0 database. After submission of job it returns the list of peptides.

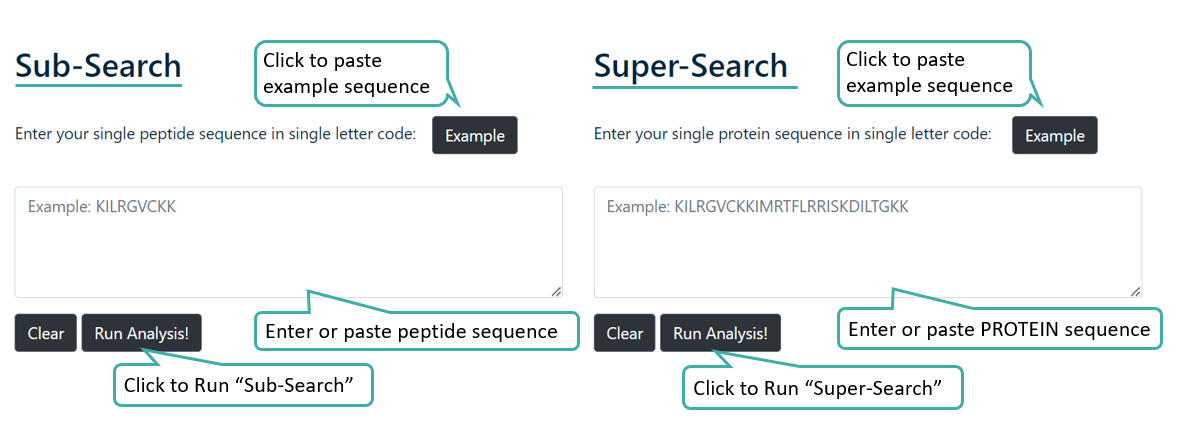
Mapping
User can select either SuperSearch to search for query PROTEIN sequence against peptides of CancerPPD or select SubSearch to search for query PEPTIDE sequence against the peptides of CancerPPD 2.0.
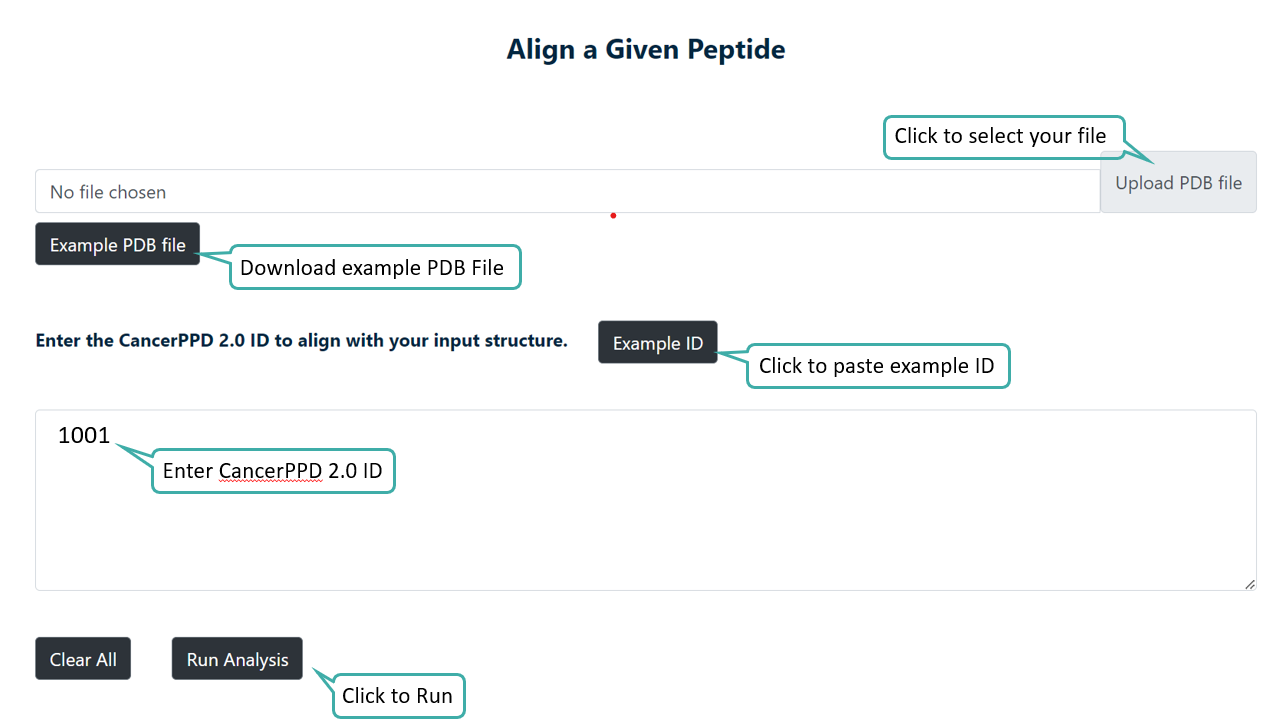
Structure Alignment
User can align their PDB structure with any of the CancerPPD 2.0 Structures
Alignment Result

API
This section describes how this website's data can be accessed with programs. A variety of data
available on CancerPPD 2.0 is accessible using simple URLs (REST) that can be used in
programs.
The CancerPPD 2.0 REST API returns the response in JSON (JavaScript Object
Notation) format. Users can parse the JSON format to suit their requirements.
HTTP Status Headers
Upon sending a request to the server the following HTTP response headers are returned by the CancerPPD 2.0 REST API:
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 200 | The request was processed successfully. |
| 400 | Bad Request. Invalid data type. |
| 404 | Not Found. The requested data doesn't exist. |
| 500 | Internal server error. Most likely a temporary problem, but if the problem persists please contact us. |
Query Fields
The CancerPPD 2.0 REST API offers access to the data through three distinct query fields: cancer type, cell line, and peptide sequence. Users can select from a diverse array of options within each field, enabling targeted retrieval of relevant data. Specifically, the cancer type query field encompasses 15 distinct cancer type parameters, while the cell line query field provides access to data from 45 different cell lines, contingent upon their significance within the database. Furthermore, the peptide sequence query field allows users to refine their search based on two parameters: Natural or Modified.
| Query Field (..dataType) | Parameter (..dataValue) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Cancer Type (cancer_type) | Breast Cancer, Lung Cancer, Ovarian Cancer, Cervical Cancer, Colon Cancer, Skin Cancer, Blood Cancer, Prostate Cancer, Liver Cancer, etc. | User can access data corresponding to particular cancer type, this will return all the entries for the selected cancer type. |
| Cell Line (cell_line) | MCF-7, A-549, HeLa, PC-3, HepG-2, MDA-MB-231, HCT-116, Jurkat, K-562, MDA-MB-435S, HT-1080, DU-145, HL-60, Caco-2, HMLER, etc. | User can access data corresponding to particular cell line, this will return all the entries for the selected cell line. |
| Peptide Sequence (seq) | Natural, Modified | Users can access data based on their selected parameter. Selecting "Natural" will retrieve entries featuring sequences composed solely of natural amino acid residues, and devoid of any chemical modifications. Conversely, selecting "Modified" will retrieve entries characterized by sequences containing non-natural residues or having any chemical modifications. |
Return Fields
Once the request has been processed successfully, the CancerPPD 2.0 REST API returns the data in JSON format. The response data consists of 16 fields:
| Return Field | Description |
|---|---|
| CancerPPD 2.0 ID | Unique identifier in the CancerPPD 2.0 database for that entry. |
| PMID | Article PMID corresponding to that entry. |
| Year | Year of publication of that entry. |
| Sequence | Sequence of the peptide. |
| Name | Name of the peptide. |
| Length | Length of the peptide. |
| Linear/Cyclic | Conformation of the peptide. |
| Chirality | Sterechemistry of the peptide. |
| Chemical Modifications | Whether the peptide contains any non-natural residues or any other chemical modifications. |
| C-Ter Modifications | Whether the C-terminal end of the peptide contains an entity or it is free. |
| N-Ter Modifications | Whether the N-terminal end of the peptide contains an entity or it is free. |
| Cell Line | Anticancer property of the peptide tested against which cell line. |
| Cancer Type | The cancer type corresponding to that cell line. |
| Assay | Type of assay used to measure the anticancer activity of the peptide. |
| Test Time | Time after which the anticancer activity was measured or found to be significant. |
| Tissue Effected | The tissue effected corresponding to that cancer type. |
CURL
cURL, short for "Client URL," is a command-line tool and library for transferring data with
URLs. It supports a wide range of protocols, including HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, FTPS, SCP, SFTP,
LDAP, TFTP, and many others. Example Command:
curl -X GET "https://webs.iiitd.edu.in/cancerppd2/api/api.php?dataType=cell_line&dataValue=A-549"-X flag is used to specify the HTTP request method. HTTP requests typically use methods such as GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc. CancerPPD 2.0 REST API allows only GET request method.
wget
wget is a command-line utility for downloading files from the web. It supports downloading
files via HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP protocols in Linux environments. Example Command:
wget "https://webs.iiitd.edu.in/raghava/cancerppd2/api/api.php?dataType=cell_line&dataValue=A-549"
How to use ?
To access the data programmatically using CancerPPD 2.0 REST API, user simply needs to select the query field and its corresponding query term and hit "Execute".
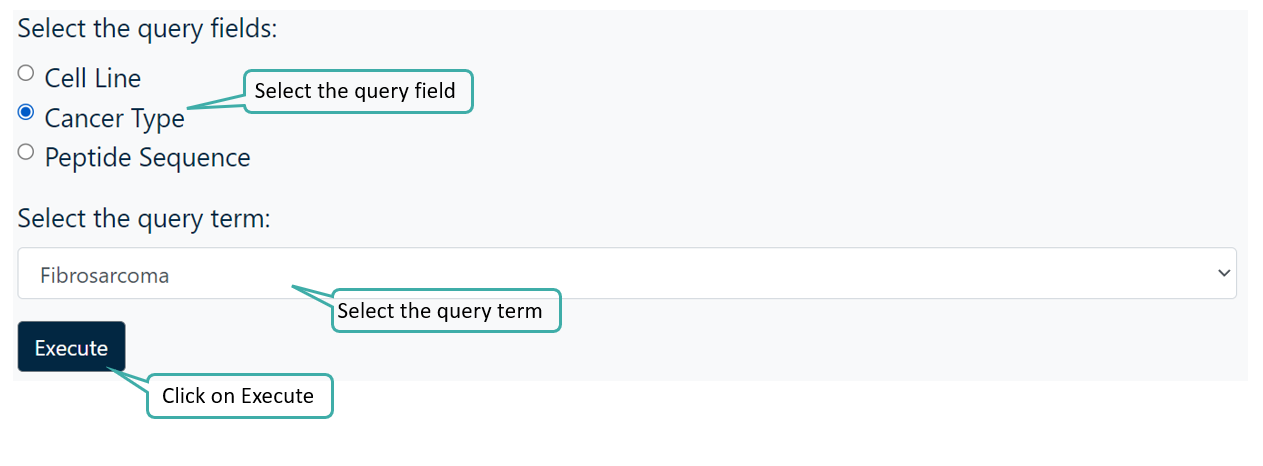
After clicking "Execute" the output will contain the cURL command, wget command, request URL and the server response.

Python Example
Below is a very simple example of how to use the CancerPPD 2.0 REST API using Python. It sends a GET request to the API endpoint, retrieves the JSON response containing data, and parses it into a pandas DataFrame for further analysis. This example demonstrates the basic process of accessing data from the CancerPPD 2.0 REST API and manipulating it within a Python environment.
import requests
import pandas as pd
# Define the URL for the API request
url = 'https://webs.iiitd.edu.in/raghava/cancerppd2/api/api.php?dataType=cancer_type&dataValue=Fibrosarcoma'
# Send a GET request to the API
response = requests.get(url)
# Check if the request was successful (status code 200)
if response.status_code == 200:
# Print the JSON response from the API
print(response.json())
# Parse the JSON data and store it in a pandas DataFrame
json_data = response.json()
df = pd.DataFrame(json_data['data'])
# Visualize the DataFrame
print(df.head()) # Display the first few rows of the DataFrame
else:
# Print an error message if the request was not successful
print('Error:', response.status_code)
