|
T1DM is a serious condition in which insulin producing β-cells in the pancreas are destroyed. Identification of T1DM associated peptides is an crucial step in understanding the fate of disease. First time an attempt have been made to develop method for predicting T1DM associated/non-T1DM associated peptides/epitopes.
The prediction server for T1DM Associated peptide/epitopes has been designed in a very user-friendly manner. Here, on this page, user can get the details of all the algorithms and procedures exploited in the different modules. |
|
Dataset UsedPositive Dataset:Updating soon..!Negative dataset:Updating soon..! |
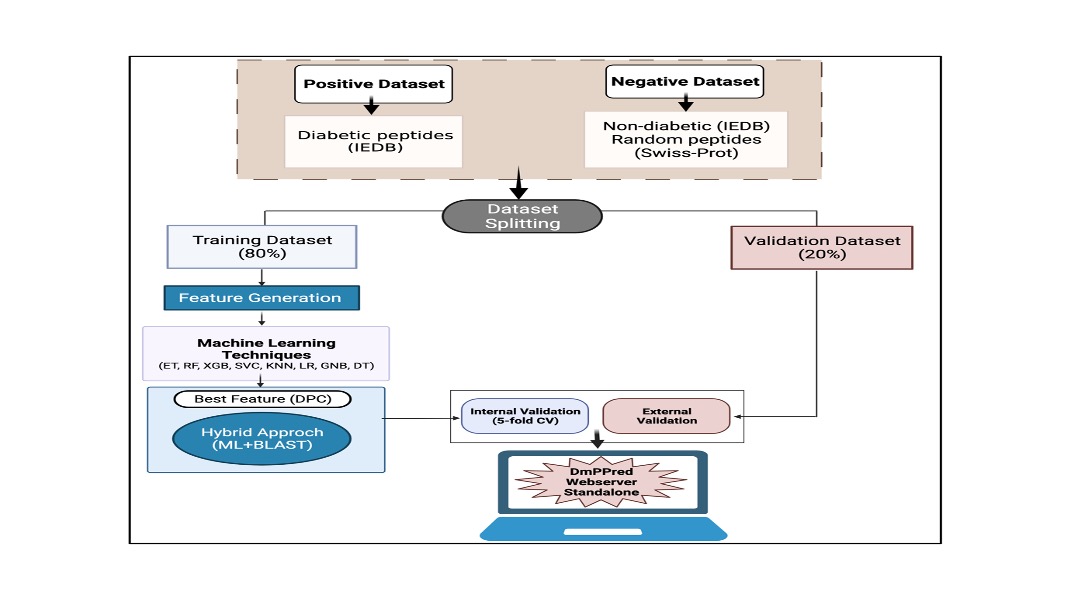
This algorithm of the server is relies on the following three models:
Prediction modelThe "Predict" module provides the facility to the user to classify T1DM associated peptides from non-T1DM associated peptides. User can provide multiple sequences as input to the server to predict the given peptide is T1DM causing/non-T1DM causing. In this study we used various machine learning techniques to develop prediction modules.Design modelIn this study, "Design" module is used to create all possible analogs/mutants of the input sequence and identify the best analog which can be diabetic. Usign various machine learning techniques it can predict wheather mutants can be T1DM associated or non-T1DM associated.Scan modelIn this study, we incorporated three scan modulesI) Protein Scan: Aim of this approach is to identify T1DM causing regions in the protein sequence, which can futher removed or altered. II) Motif Scan: Aim of this approach is to discover motifs or patterns in T1DM causing and non-T1DM causing epitopes. In this study we used a powerful pattern discovery software MERCI. First we identified motifs are exclusively found in T1DM peptides and not present in non-T1DM peptides. Similarly we identified motifs in non-T1DM peptides which are absent in T1DM peptides. These novel motifs used for discriminating T1DM and non-T1DM peptides. III) BLAST Scan:“Blast Search” module is based on a similarity search method, i.e., Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST). The input query sequence is searched against the database of known T1DM peptides. A query sequence is predicted as T1DM associated if found match or hit in the database; otherwise, it is predicted as non-T1DM associated peptide. |