Applications of CancerDP |
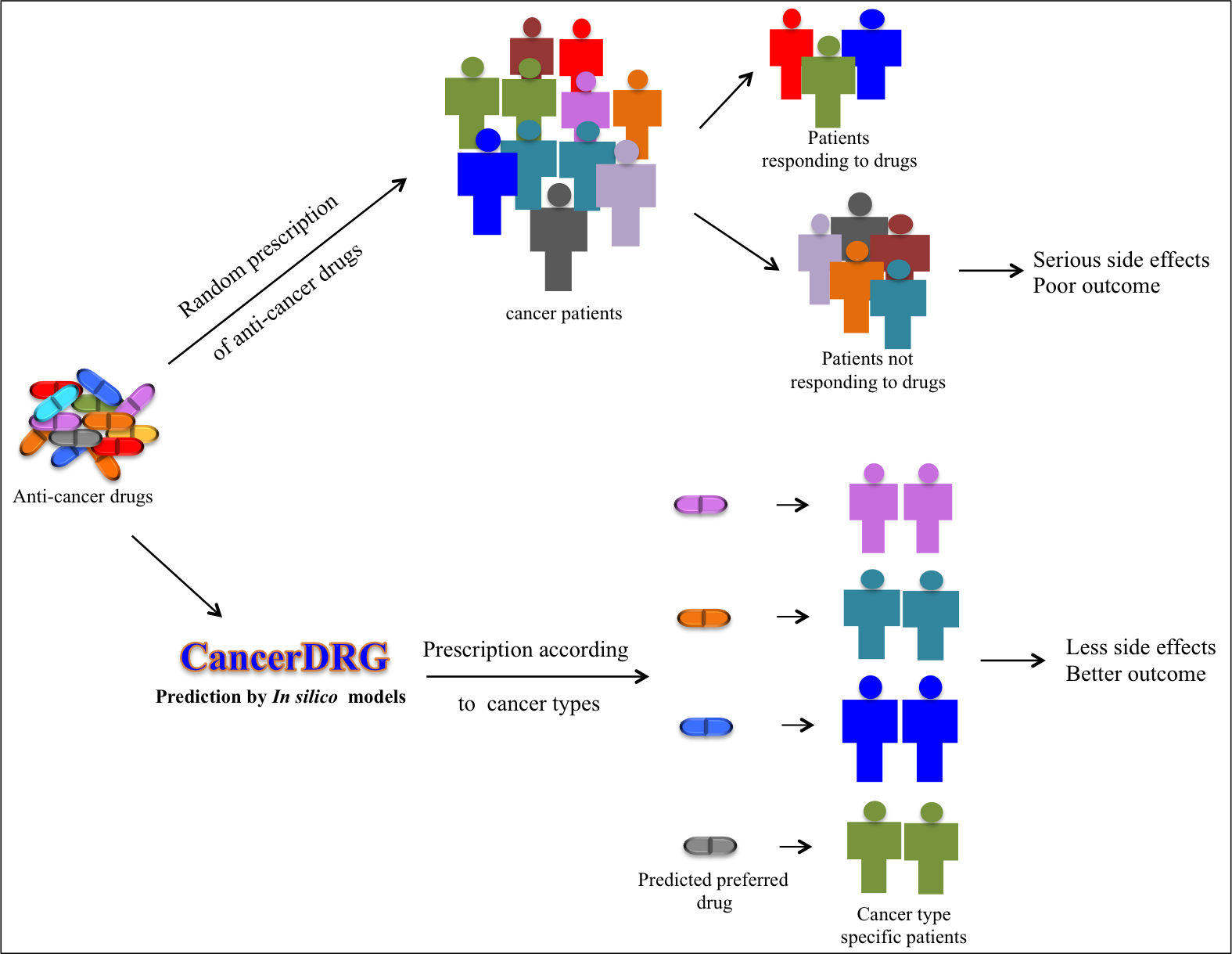
|
Drug Prioritization Prediction based on Machine Learning Method1: Based on Limited Genes (30)- Mutation1This page is designed to provide drug prioritization prediction with limited number of genes. With a limitation of low performance, user just needs to submit mutational status of given 30 genes. For prediction, the mutational information of all the 30 genes is MANDATORY. The “selected” genes and “unselected” genes are considered as “mutated” and “not mutated” respectively.1: Based on Genome- Mutation2This tool is developed for users having mutational information of whole genome. With higher number of genes, this module should be selected for better performance. In particular, the prediction models are developed on only 268 genes as given in the list. For the convenience of user, user has to submit mutation information of whole genome as given in example file. The submission mutation file needs to have HUGO symbol of gene in first column and IUPAC annotation of mutation in second column (as provided in MAF or Mutation Annotation File after sequencing).1: Based on Variation of GenomeThis tool is developed for users having gene variation information of whole genome. In this tool, the prediction models are developed on 420 unique signature genes as given in the list. For the convenience of user, user has to submit gene variation information of whole genome as given in example file.1: Based on Expression of Limited (Top 50 correlated) Genes- Expression1 and Whole Genome- Expression2This module incorporates predictive modeling of cancer drugs using expression of genes. Among two kinds of models, the first model (based on top 50 correlated genes) requires expression of just 50 genes, while second model (based on 619 significant genes) requires expression of whole genome. The expression-based models based on 619 genes performed best among all other features in our study, providing even better prioritization of cancer drugs. This tool requires mRNA expression data on Affymetrix Human Genome U133 Plus 2.0 arrays with background correction done by RMA (Robust Multichip Average) and quantile normalization.1: Based on CNV of Whole Genome- CNVIn this module, drug prioritization can be done by pridictive models based on copy number variation. The models are based on 430 unique genes for all the 24 drugs. By submitting the CNV profile in required format as given in example file, on can predict the most preffered drug among 24 anticancerous drugs. The required CNV data should be inormalized log2(CN/2), segmented with circular binary segmentation (CBS) algorithm as given by authos of CCLE.Drug Calculator based on Probability Method1: Based on Mutation of Individual GeneThe purpose of this tool is to find out the best drug for a patient based on mutation in query genes. This tool is based on the probability of finding mutations in a gene in resistant vs. sensitive cell lines of our dataset. Since this tool is based on probability, contribution of every single gene can be looked for resistance. Here user just needs to submit comma seperated HUGO symbols as query genes.1: Based on Expression of Individual GeneThe purpose of Expression-based Drug Calculator is to find out the best drug for a patient based on expression of query gene. This tool is based on the difference of expression between resistant and sensitive cell lines.1: Based on CNV of Individual GeneThe purpose of CNV-based Drug Calculator is to find out the best drug for a patient based on Copy Number Variation of query gene. This tool is based on the difference of CNV between resistant and sensitive cell lines.Genome Submit1: Based on VariationThe purpose of this tool is to predict drug by annotating the general variation, present in a newly sequenced cancer sample. For this purpose we require Variant Call Format (VCF) file , which is one of the most accepted format for storing gene sequence variations. Our module process the VCF file with the help of ANNOVAR package to extract and annotate the general variations, which are then used in prediction of priority of anticancerous drugs.1: Based on MutationThe purpose of this tool is to predict drug by annotating the deleterious mutations, present in a newly sequenced cancer samples. For this purpose we require Variant Call Format (VCF) file , which is one of the most accepted format for storing gene sequence variations. Our module process the VCF file with the help of ANNOVAR package to extract deleterious mutations, which are then used in prediction of priority of anticancerous drugs.Browse for Signature genes1: Significant Genes based on MutationThe pupose of this tool is to find out the significance of a gene mutation in terms of IC50 for given drugs. This tool is based on the difference of IC50 of mutated and normal cell lines for that particular gene.The occurance of mutation in every single gene may lead to resistance or sensitivity. The first column (WILD) shows the average IC50 of mutated cell lines for that gene and same of sensitive cell line in second column (MUT) for normal cell line. The third column (PVALUE) of every gene shows the significance of difference between mean IC50s of mutated and wild type cell lines for that gene. For example IL1RN mutated and normal cell lines show highest difference in IC50 thus IL1RN gene mutation may lead to 17AAG resistance.2: Significant Genes based on ExpressionThe pupose of this tool is to find out the significance of high expression of a gene on IC50 for given drugs. This tool is based on the difference of IC50 of cell lines having high and low expression for that particular gene.Expression levels of a certain gene may lead to resistance or sensitivityfor a particular drug. The first column (R) shows the average IC50 of resistant cell lines (IC50 >=0.5 and gene expression value >=12) and same of sensitive cell line in second column (S) for cell lines (IC50 <=0.5 and gene expression value >= 12). The third column (PVALUE) of every gene shows the significance value of difference between these IC50s.3: Significant Genes based on CNVThe pupose of this tool is to find out the significance of copy number variation (CNV) of a gene on IC50 for given drugs. This tool is based on the difference of average IC50 of cell lines having CNV value <=-1 or >=+1 for that particular gene.CNV of a certain gene may lead to resistance or sensitivityfor a particular drug. The first column (R) shows the average IC50 of resistant cell lines (IC50 >= 0.5) and same of sensitive cell lines (IC50 < 0.5) in second column (S). The third column (PVALUE) of every gene shows the significance value of difference between these average IC50s.4: Correlated Genes based on ExpressionThe pupose of this tool is to find out the most correlated genes with IC50 for given drugs. This tool is based on the correlation of expression of genes with IC50 of cell lines for that particular gene. Each column shows correlation for that particular drug.FOr example IGLV3.25 and DUSP6 genes are highly correlated with Panobinostat and PD0325901 drugs respectively.5: Correlated Genes based on CNVThe pupose of this tool is to find out the significance of a gene mutation in terms of IC50 for given drugs. This tool is based on the difference of IC50 of mutated and normal cell lines for that particular gene.The occurance of mutation in every single gene may lead to resistance or sensitivity. The first column (-S) shows the average IC50 of mutated cell lines for that gene and same of sensitive cell line in second column (-wild) for normal cell line. The third column (-DIFF) of every gene shows the difference between these IC50s. For example IL1RN mutated and normal cell lines show highest difference in IC50 thus IL1RN gene mutation may lead to 17AAG resistance. |
