Testing of ComPred( hybrid approach )on PRAME protein:-
The aim behind the development of nHLAPred is to effectively reduce number of wet lab experiments involved in the identification of potential T
cell epitopes or suitable vaccine candidates.To test whether the aim is achieved or not authors applied the server on such antigenic protein whose MHC binders and CTL epitopes are experimentally proved.We have choosen the PRAME protein whose MHC binders and CTL epitopes are recently identified by Kessler et al., 2002. The sequence of PRAME antigenic protein was obtained from SWISSPROT database.
MHC binders identification:-The ComPred part of server has been used in identification of HLA-A*0201 binding 19 high affinity and 27 intermidiate affinity MHC binders of PRAME protein.The server has been used at different cutoff scores.The detailed performence of server in correctly identifying the MHC binders is shown in
TableS5.The method correctly identified 73% high affinity and 81% intermediate affinity binders at default cutoff score 0.5.The default cutoff score means a value at which the senstivity and specificity are nearly equal.This proves that it is worth to use the server for MHC prediction.
HLA-A*0201 restricted potential CTL epitope identification:-Kessler et al., 2002 has demonstracted that MHC binders having proteasomal cleavage site at C terminal are mostly recognised by CTL cells.They have identified four regions from PRAME protein which have CTL epitopes. Thus, we have used this server in identification of experimentally proved antigenic regions. The server ComPred has been applied at default cutoff score of ANN and various thresholds of proteasomal filters. The server predict the MHC binders which have proteasomal cleavge sites at C terminal.The number of peptides predicted by above falls in regions identified as T cell epitopes by Kessler et
al., 2001, is shown in following Table. ComPred was tested on 4 regions of PRAME (A: 90-116; B:133-159; C: 290-316; D: 415-441) which were
identified as T cell epitopes by Kessler et al., (2001). The column 2 shows the number of predicted peptides and regions (in bracket), which
agree with the experimentally identified epitopes.
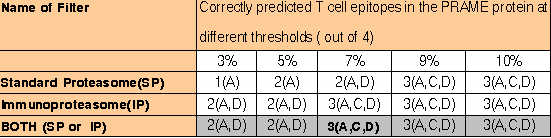
The server is able to identify 75% of experimantally identified regions at default cutoff score of method and 7% threshold of proteasomal filters.. The server is even able to identify all the experimantally identified antigenic regions at 0.01 cutoff score and 10% threshold of standard proteasome filter.This demonstrates that it is worth to use this server for scanning of vaccine candidates from complex genomes.


