Prediction of Beta Turn
Previously, group developed methods like BetaTPred, BetaTPred2 and BetaTurns to predict turns and their types in proteins. Most of existing methods have been trained on limited data (around 426 protein chains). This server BetaTPred3 have number of advatage over existing methods that includes; reliability, accuracy and turn-level prediction.
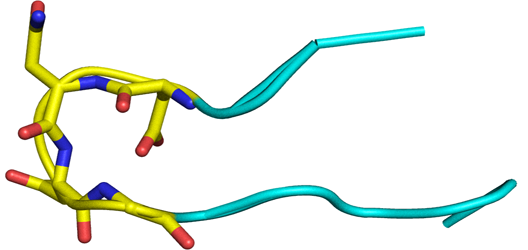
Beta Turn in proteins
Beta-turns are the most common type of non-repetitive structures, and constitute on average 25% of the residues in all protein chains. In a beta turn, a tight loop is formed when the carbonyl oxygen of one residue forms a hydrogen bond with the amide proton of an amino acid three residues down the chain. This hydrogen bond stabilizes the beta bend structure. A beta turn can reverse the direction of its peptide chain.
Propensity based Beta Turn prediction
In the past statistical methods were developed to predict the beta turns based upon propensity score of beta turn. The propensity score was calculated using few hundered PDBs. We have calculate new propensity score using ~18000 PDBs. Users can predict beta turns based upon various position based propensity score. Click here to »Submit »
Designing of Beta Turn
For the first time, we have developed a module thats helps user in understanding the positional preference of pairs of amino acids. First, user sequence is mapped and various propensity score are shown for all possible tetrapeptide. Second, the module performs all possible mutation in a tetrapeptide, either to increase or decrease its beta turn formation probability. Click here to »Submit »
Prediction of Beta Turn Type
In the past numerous methods were developed to predict the beta turn types. Using the turn level approach we have significantly improved the prediction accuracy of beta turn types. To predict beta turns types in your protein click »Submit »
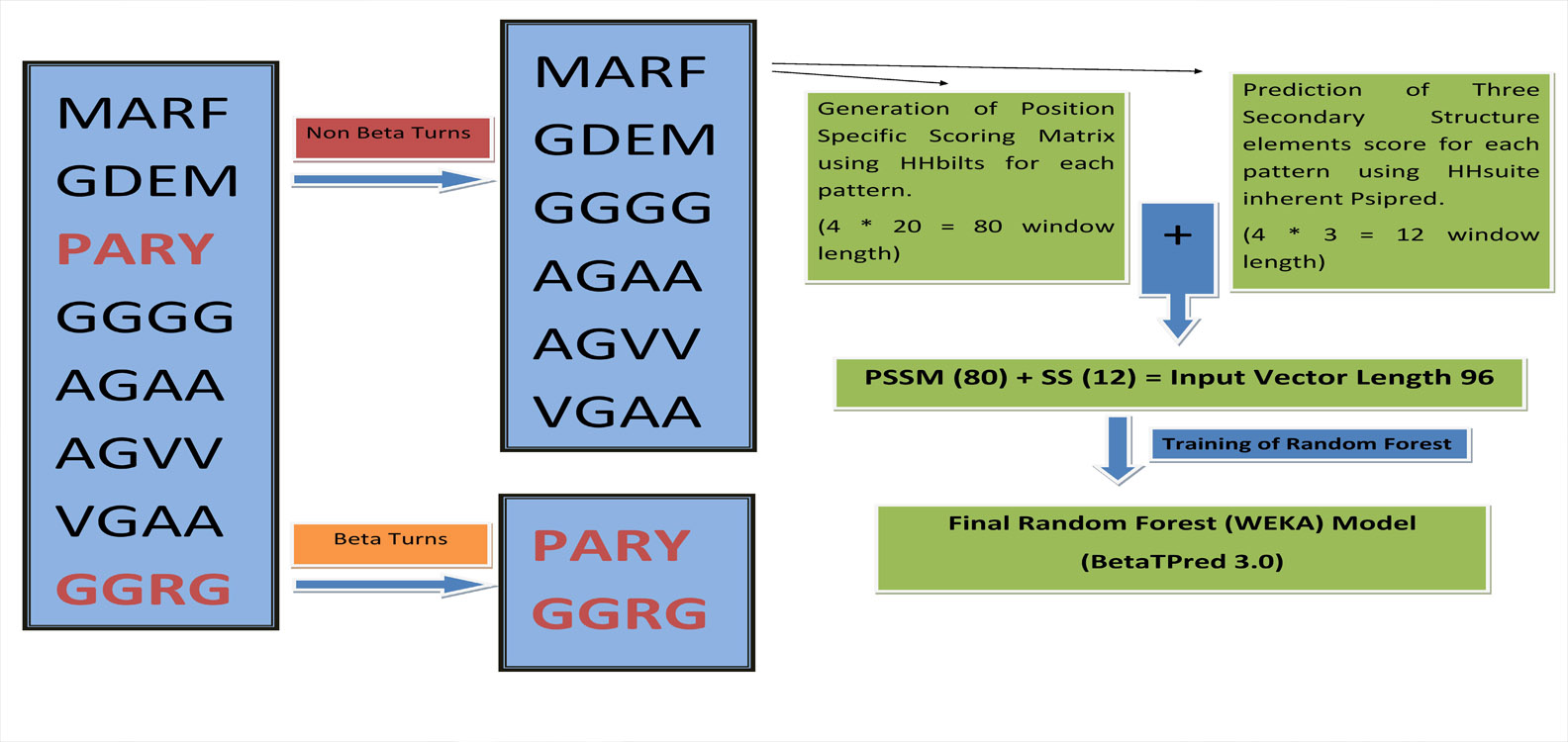
Algorithm
We have developed a algorithm that predcit complete beta turn, earlier algorithm predict the residue that are present in beta turn. They can predict a residue to be beta turn residue, even its neighbouring residue are non beta turn. Our algorithm has overcome all these limitation and can predict only four consecutive beta turn residues.
More »


