Search
This section provides information about how to perform searches.
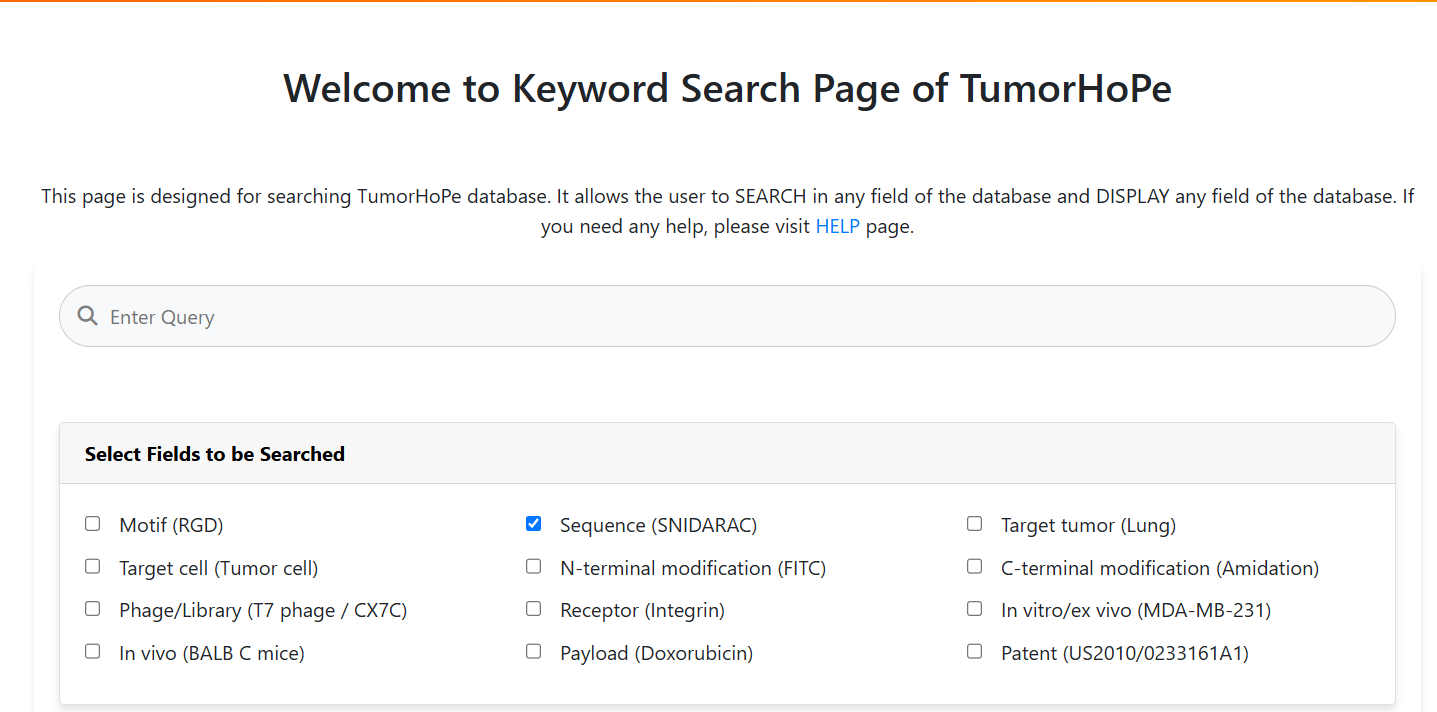
Keyword Search
This option provides a straightforward way to search using a single word. Users can enter a sequence (e.g.,
CSNIDARAC), motif (e.g.,
WYY), target tumor (e.g.,
Breast cancer), target cell (e.g.,
Endothelial cell), or cell lines (e.g.,
MDA-MB) as used in the experiments.
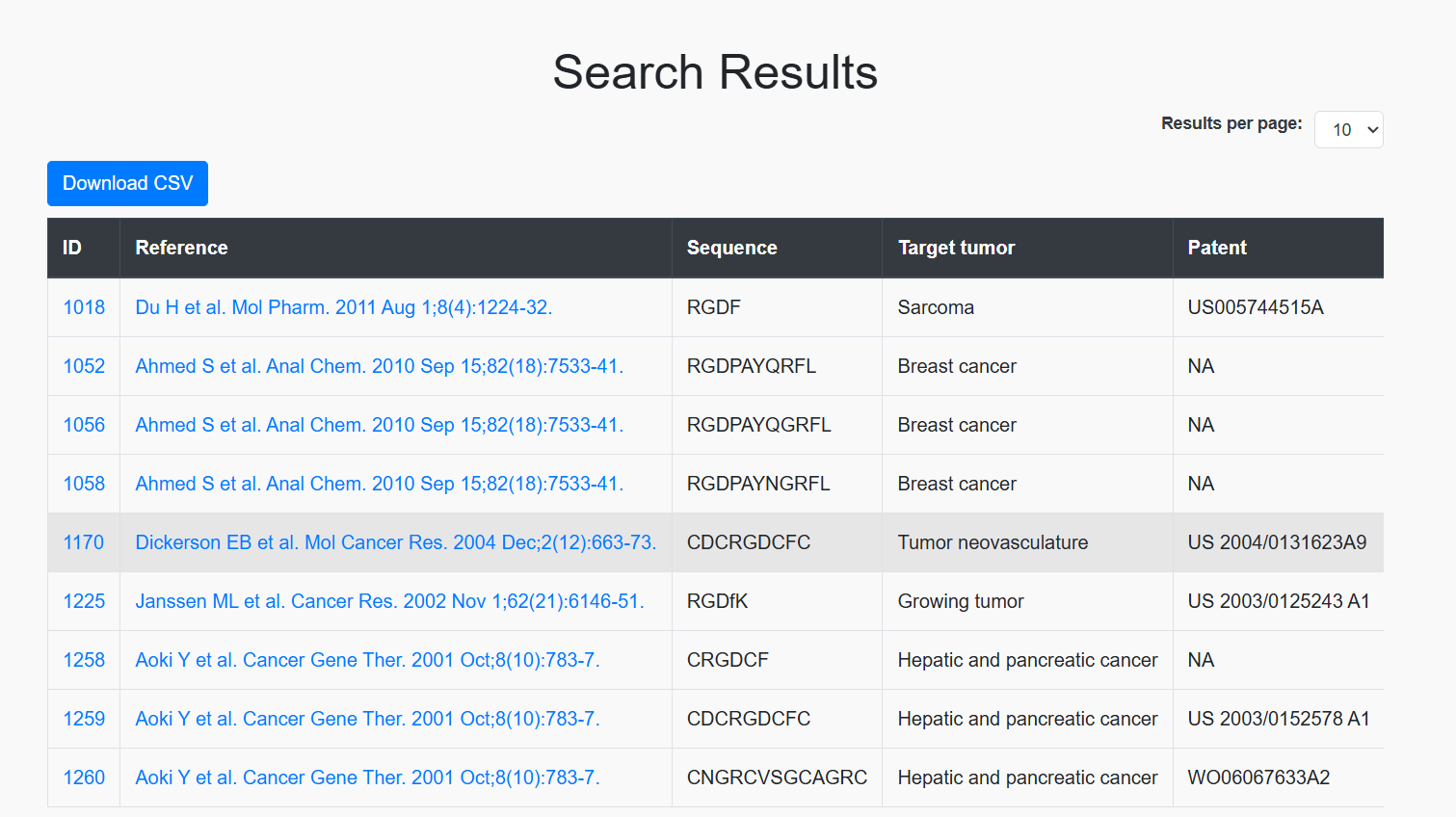
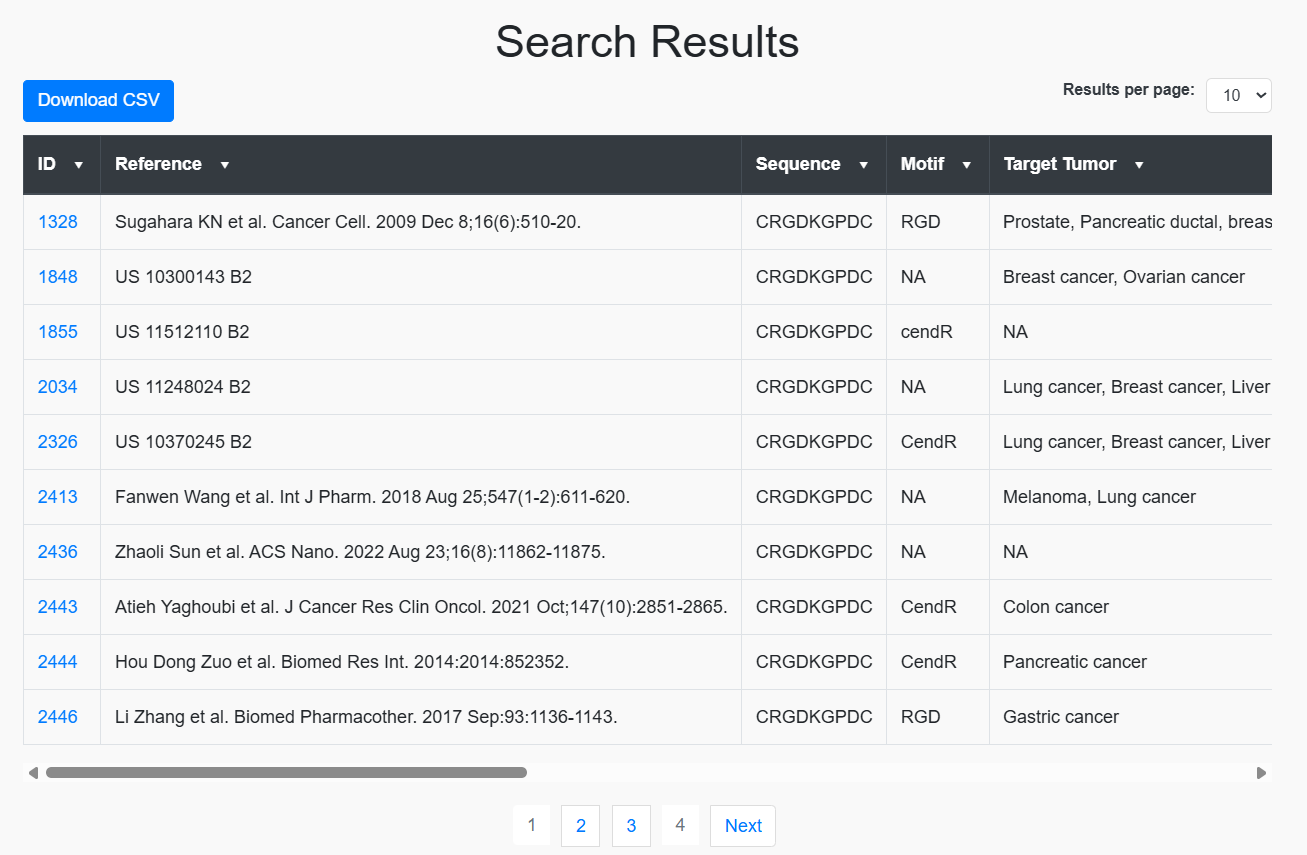
The results will be displayed based on the selected fields, such as the sequence, research article details, PMID, etc.
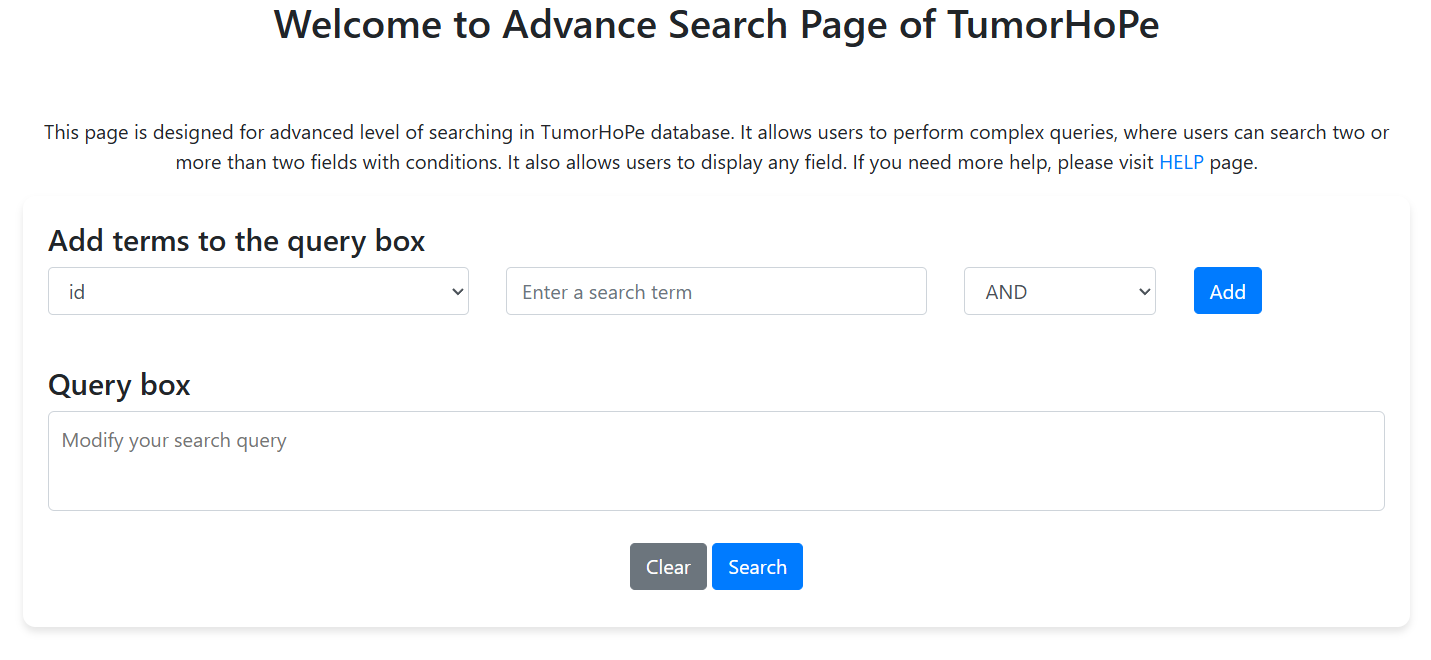
Advance Search
This page allows complex queries in the TumorHoPe database using multiple fields and logical operators.
- Select a field, enter a value, and choose an operator (AND, OR, NOT).
- Add terms to build your query.
- Edit the Query Box directly if needed.
- Click Search to run or Clear to reset.
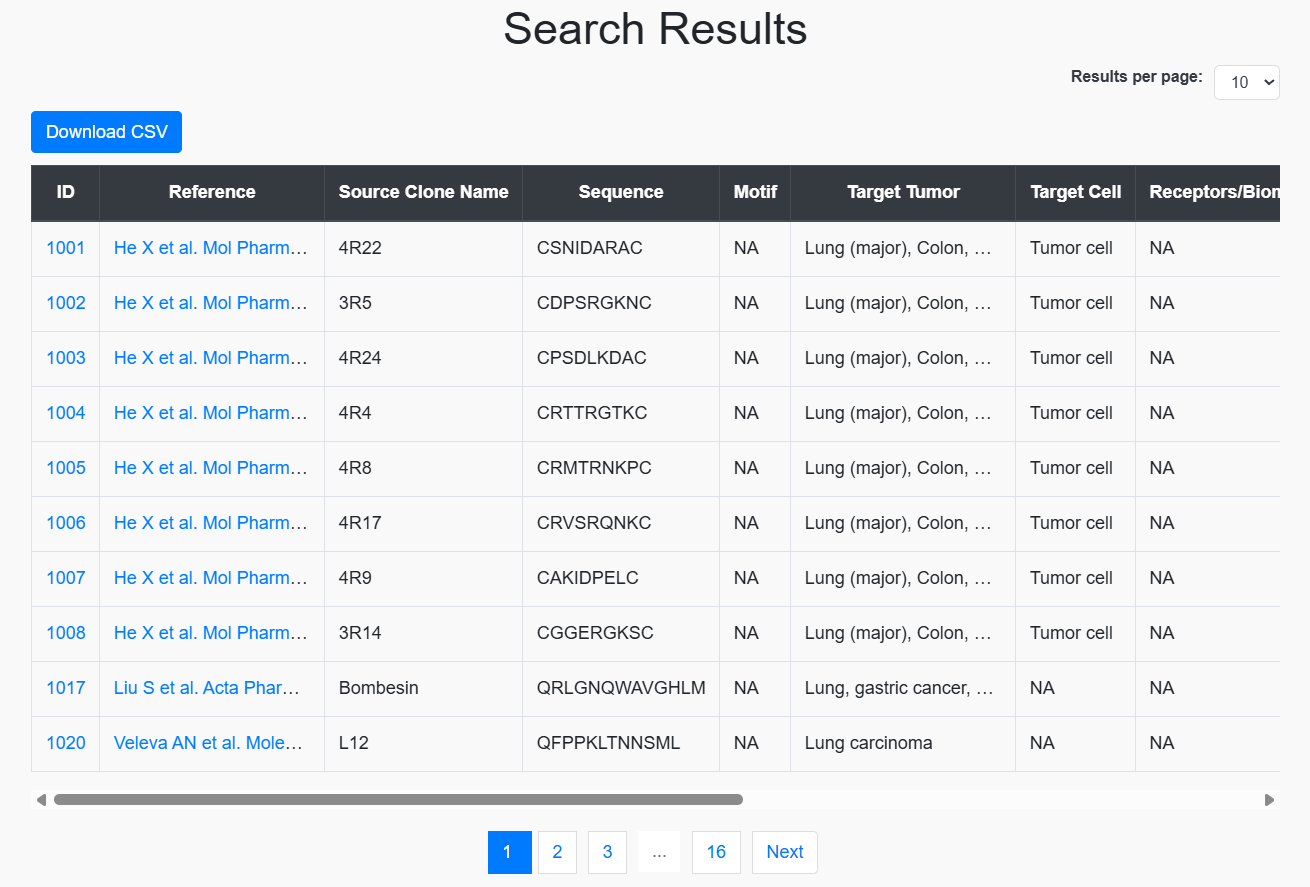
- Download results using Download CSV.
For full documentation, visit the HELP page.
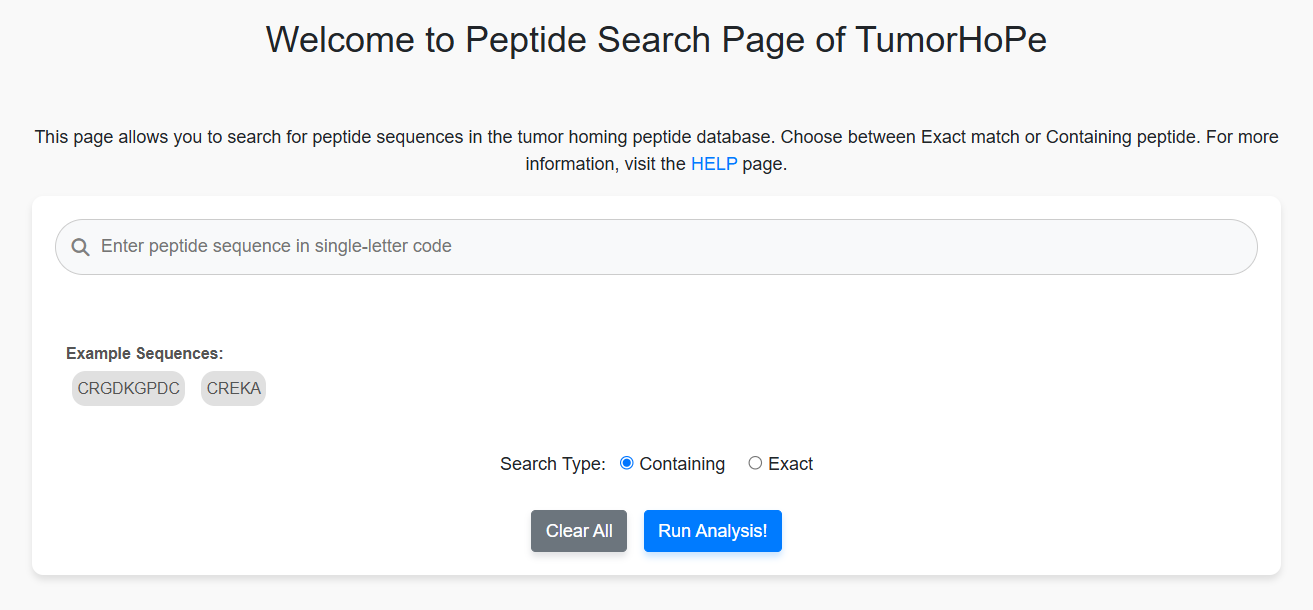
Peptide Search
Users can search a query sequence against the entire database. The results will display either peptides that exactly match the query or peptides that partially match the provided sequence.
Browse
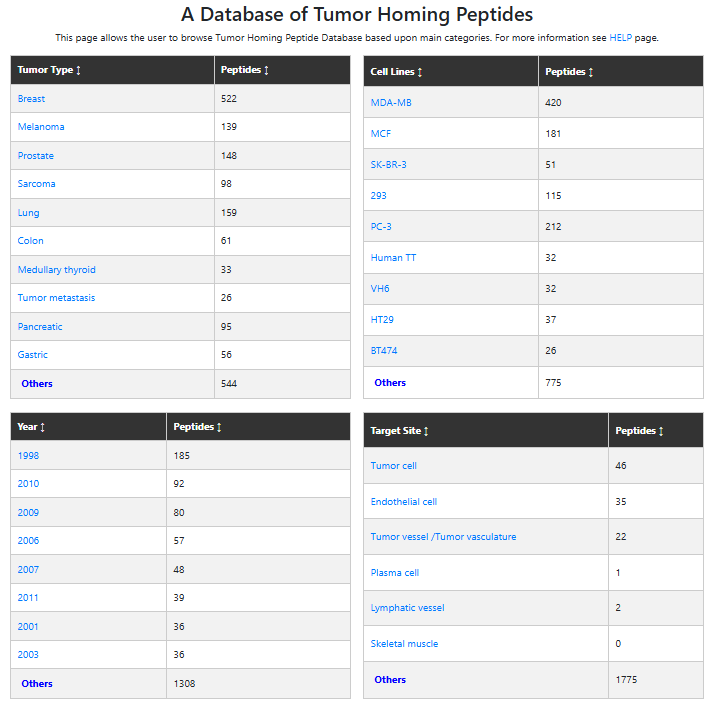
This section provides multiple options to explore tumor homing peptides based on various criteria.
Major Fields
This interface enables users to browse the database by the following key fields:
- Target Tumor
- Cell Line
- Year of Publication
- Target Site
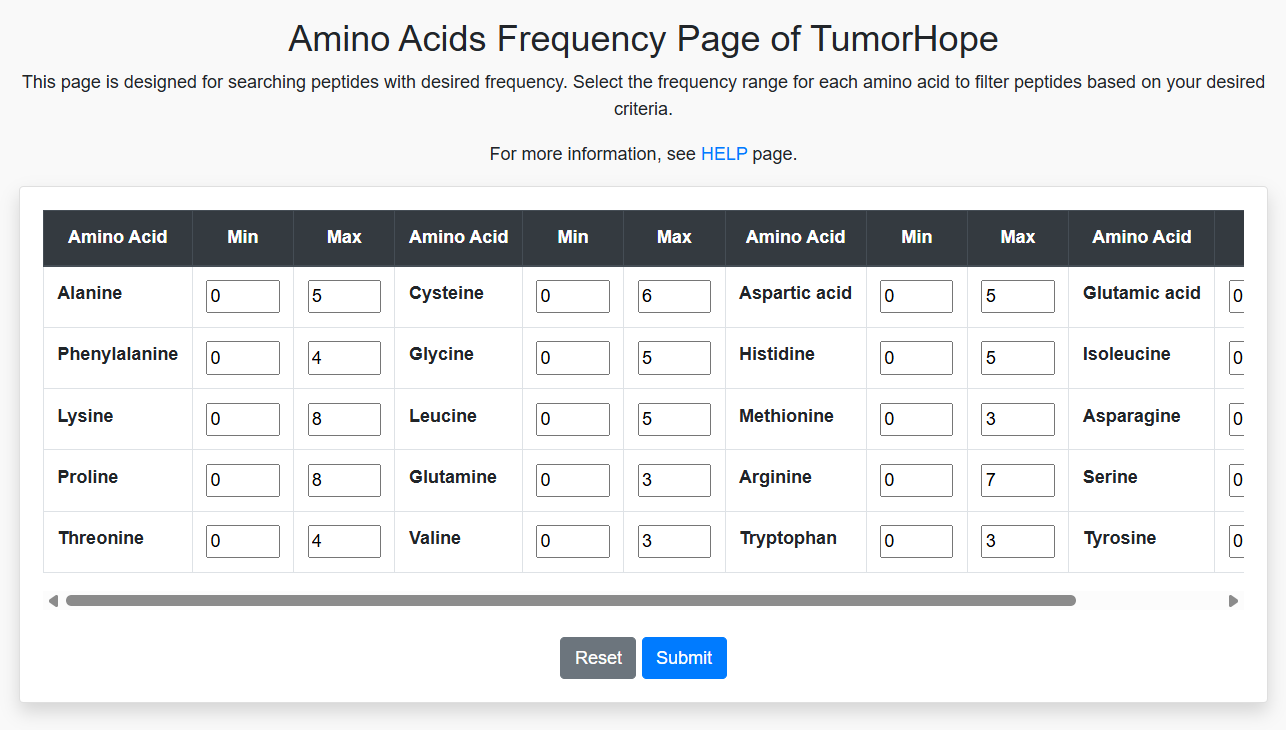
Amino Acid Frequency and Composition
Filter sequences by amino acid frequency and composition. For example, setting Lysine values between 3 and 23 will retrieve all sequences with Lysine counts in that range. You can combine this with other amino acid criteria (e.g., Glycine between 4 and 18) to further refine the results. This method also applies to filtering by amino acid composition as well as physical property frequency and composition.
Physicochemical Property Frequency and Composition
Retrieve tumor homing peptides based on the frequency of specific residue types. You can:
- Filter by residue types such as positive charge, negative charge, or polar residues.
- Adjust default minimum and maximum values to customize your search range.
- Example: Set an aromatic property range between 2 and 8 to display all peptides within that range.
- Combine multiple property criteria (e.g., aromatic property and positive charge) for more refined results.
Physicochemical Property Values
Display tumor homing peptides that fall within user-defined ranges for the following properties:
- Hydrophobicity
- Hydrophilicity
- Net Charge
- Isoelectric Point
- Molecular Weight
Enter the desired minimum and maximum values for each property to retrieve peptides that match your criteria.
Structure
This section allows users to explore structural information of tumor homing peptides based on secondary structure and 3D models.
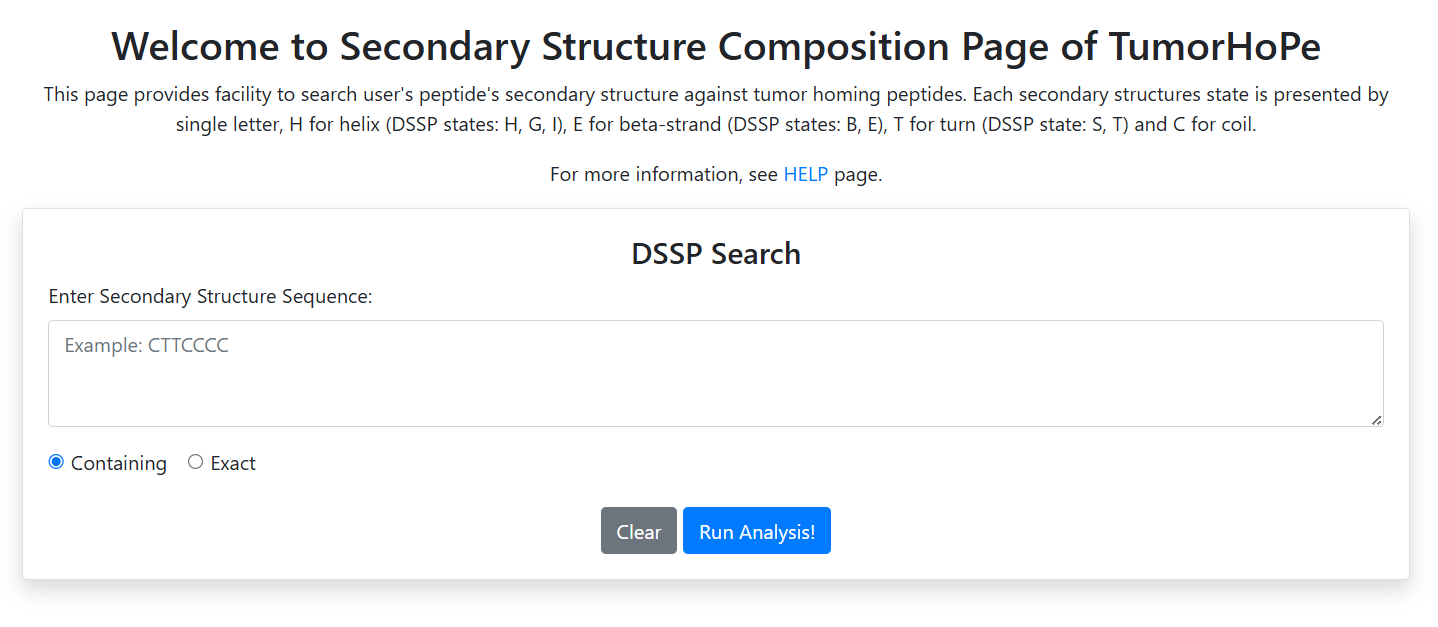
Secondary Structure Composition
Retrieve peptides based on the percentage composition of four different secondary structural states:
- Helix (H)
- Beta Sheet (E)
- Turn (T)
- Coil (C)
Define the minimum and maximum percentage values for each structural type to filter the results.
Secondary Structure Prediction
Submit a peptide sequence from the database to receive its predicted secondary structural state.
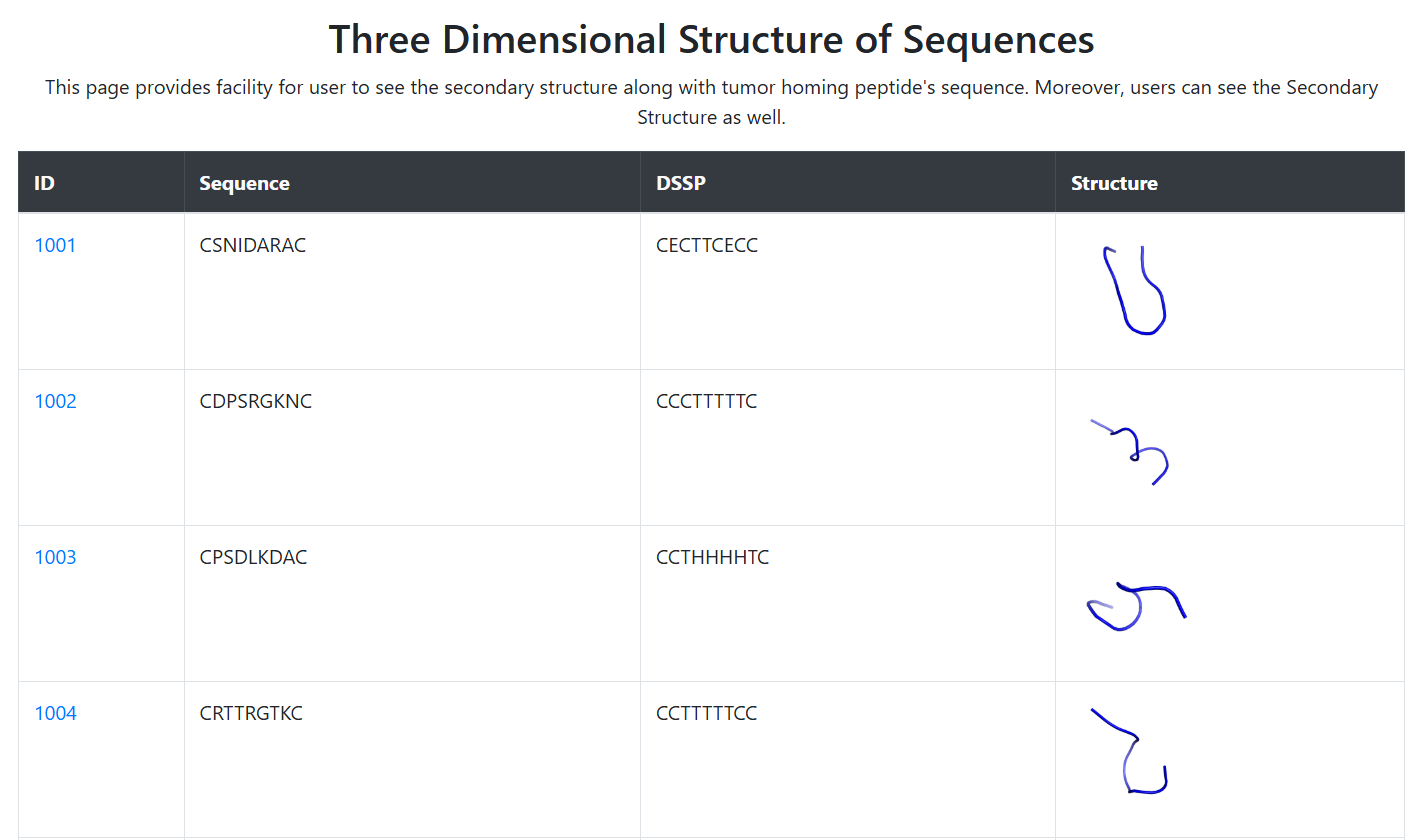
3D Structures
Three-dimensional structures of all tumor homing peptides have been predicted using the PEPstr tool.
Tools
This section provides computational tools for analyzing and comparing peptide sequences against the Tumor Homing Peptide database.
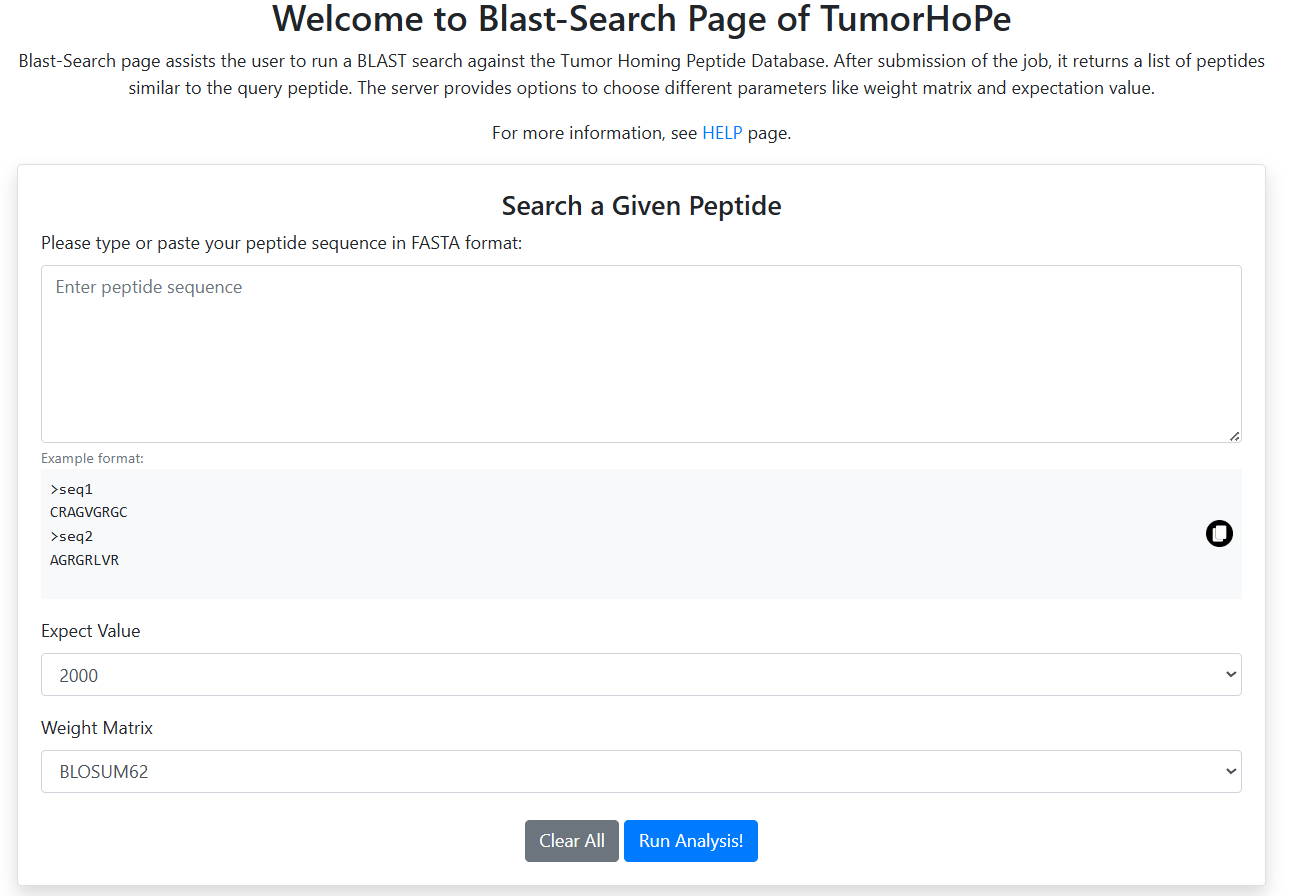
BLAST 🔗
Perform a similarity-based search of a query sequence against the Tumor Homing Peptide database using BLAST.
- Enter the query sequence using single-letter amino acid codes.
- The tool returns all peptides from the database that show similarity to the query.
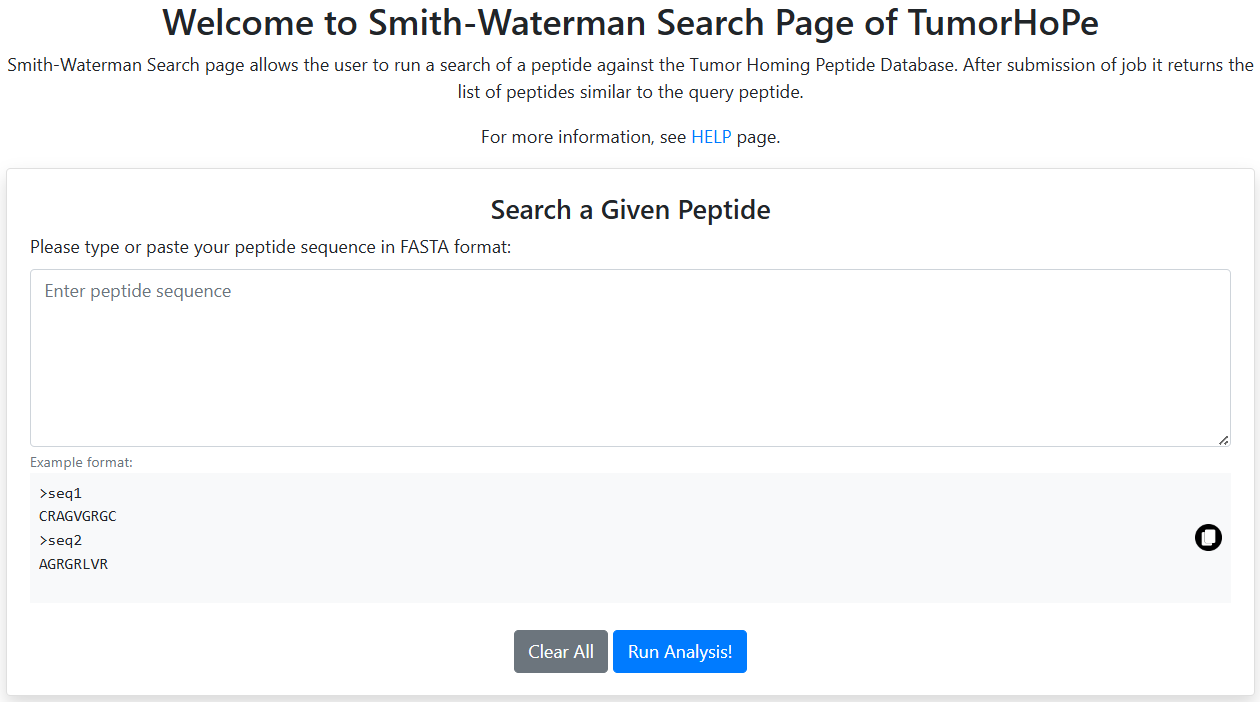
Smith-Waterman
This tool identifies regions of local similarity between the query peptide and peptides in the database.
- Performs pairwise alignments by comparing all possible segments.
- Optimizes similarity scores to provide precise alignment results.
Identical Residues
Compares the query sequence with each peptide in the database to determine exact residue matches.
- The sequence is aligned step-by-step with all database peptides.
- The tool returns the count of identical residues for each pair.
Peptide Mapping
Slide the query peptide across all database sequences to find the best alignment with the highest number of identical residues.
Physical Properties
Calculate physical properties of a given peptide, including:
- Hydrophobicity
- Hydrophilicity
- Net Charge
- Isoelectric Point
- Molecular Weight
Description of Fields
This table summarizes the various fields included in the Tumor Homing Peptide database along with their descriptions and examples.
| Field Name | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| ID | Unique identifier assigned to each tumor homing peptide in the database. | 1025 |
| REFERENCE | Research article reference including author(s), journal, year, volume, and page numbers. | He X et al. Mol Pharm. 2011 Apr 4;8(2):430-8. |
| SOURCE/ORIGIN | Source from which the peptide was derived. | Phage Display |
| MOTIF | Specific sequence motif identified in the peptide. | NGR |
| TARGET TUMOR | Target tumor against which the peptide was developed. | Lung |
| TARGET CELL | Targeted cell type for the peptide. | Endothelial cell |
| RECEPTOR | Receptor that the peptide binds to or interacts with. | Aminopeptidase N |
| END MODIFICATION | Modifications made to the peptide termini (N-/C- terminus). | FITC labeling at N-terminus & amidation at C-terminus |
| In vitro/ ex vivo | Cell lines used for in vitro or ex vivo experiments. | MDA-MB-231 |
| In vivo | Animal models used for in vivo studies. | BALB C mice |
| PAYLOADS | Conjugates attached to peptides for imaging or drug delivery. | Doxorubicin |
| STRUCTURE | Predicted 3D structure of peptides using Pepstr (only natural amino acids). | 3D structure |
| NET CHARGE | Net charge of the peptide. | +1 |
| HYDROPHOBICITY | Overall hydrophobicity score of the peptide. | 33.33 |
| MOLECULAR WEIGHT | Molecular weight of the peptide. | 1025.32 |
| pI | Isoelectric point of the peptide. | 4 |
| AA FREQUENCY | Count of each amino acid present in the peptide sequence. | 5 |
| AA COMPOSITION | Percentage composition of each amino acid in the peptide. | 50.00 |
| SECONDARY STRUCTURE INFORMATION | Secondary structural states (e.g., Helix, Coil, Strand) for each residue. | Helix, Coil, Strand |
Description of Cell Lines
This table provides detailed information about the cell lines used in the Tumor Homing Peptide Database, including their source, morphology, and growth characteristics.
| Cell Line | ATCC No. | Organism | Disease | Source Organism | Morphology | Growth Properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDA-MB-231 | HTB-26 | Homo Sapiens | Adenocarcinoma | Mammary Gland | Epithelial | Adherent |
| MDA-MB-361 | HTB-27 | Homo Sapiens | Adenocarcinoma | Mammary Gland | Epithelial | Loosely Adherent |
| MDA-MB-435 | HTB-129 | Homo Sapiens | Ductal Carcinoma | Mammary Gland | Spindal | Adherent |
| MCF-7 | HTB-22 | Homo Sapiens | Adenocarcinoma | Mammary Gland | Epithelial | Adherent |
| SK-BR-3 | HTB-30 | Homo Sapiens | Adenocarcinoma | Mammary Gland | Epithelial | Adherent |
| HT-29 | HTB-38 | Homo Sapiens | Colorectal Adenocarcinoma | Colon | Epithelial | Adherent |
| BT-474 | HTB-20 | Homo Sapiens | Ductal Carcinoma | Mammary Gland | Epithelial | Adherent, patchy |
| BT-483 | HTB-121 | Homo Sapiens | Ductal Carcinoma | Mammary Gland | Epithelial | Adherent |
| HeLa | CCL-2 | Homo Sapiens | Adenocarcinoma | Cervix | Epithelial | Adherent |
| Ca Ski | CRL-1550 | Homo Sapiens | Epidermoid Carcinoma | Cervix | Epithelial | Adherent |
| A549 | CCL-185 | Homo Sapiens | Carcinoma | Lung | Epithelial | Adherent |
| A375 | CRL-1619 | Homo Sapiens | Malignant Melanoma | Skin | Epithelial | Adherent |
| PC-3 | CRL-1435 | Homo Sapiens | Adenocarcinoma | Ovary | Epithelial | Adherent |
| MDA-PCa-2b | CRL-2422 | Homo Sapiens | Adenocarcinoma | Prostate | Epithelial | Adherent |
| LNCaP | CRL-1740 | Homo Sapiens | Carcinoma | Prostate | Epithelial | Adherent |
| OVCAR-3 | HTB-161 | Homo Sapiens | Adenocarcinoma | Ovary | Epithelial | Adherent |
| H226 | 5826 | Homo Sapiens | Squamous Cell Carcinoma | Lung | Epithelial | Adherent |
| H460 | HTB-177 | Homo Sapiens | Large Cell Lung Cancer | Lung | Epithelial | Adherent |
| ZR-75-1 | CRL-1500 | Homo Sapiens | Ductal Carcinoma | Mammary Gland | Epithelial | Adherent |
| Hep G2 | HB-8065 | Homo Sapiens | Hepatocellular Carcinoma | Liver | Epithelial | Adherent |
| MIA PaCa-2 | CRL-1420 | Homo Sapiens | Carcinoma | Pancreas | Attached epithelial with floating rounded cells | Adherent |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is TumorHoPe?
TumorHoPe is a literature-based database of tumor homing peptides.
Q2. Why tumor homing /targeting peptides?
The biggest challenge of cancer chemotherapy is the lack of specificity and selectivity for the target. Peptide-based therapy such as tumor homing peptides are highly specific for their target. These peptides target either tumor cells or the microenvironment around them like blood vessels and lymph vessels.
Q3. How to search into TumorHoPe?
Users can search a peptide by name, peptide sequence, target tumor, cell lines, and PMID.
Q4. What other information one can get regarding peptide sequence?
The database provides amino acid composition, frequency, physicochemical properties like hydrophobicity and net charge, as well as secondary and tertiary structure information.
Q5. Is this database useful if users have their own query sequence?
Yes, users can use tools like BLAST, SMITH-WATERMAN, and peptide mapping. They can also obtain amino acid composition, frequency, and physicochemical properties.
Q6. Are all peptides used in the database experimentally validated?
Most peptides are obtained by using phage display, which yields clones for a particular target cell. The database provides details for clones with the highest recovery frequency.
Q7. Is tumor homing peptide a reality?
Yes, drugs are being conjugated with these peptides and are in different stages of clinical trials. For example, tTF-NGR peptide was used to treat a woman suffering from metastatic adenocarcinoma after four lines of chemotherapy.
Q8. Are there any peptides with modification?
Yes, some peptides contain modified amino acids. 'X' represents norleucine (an isomer of leucine); 'F*' represents 4-chlorophenylalanine; and lowercase letters indicate D-amino acids.
Note: In the case of bioconjugate peptides (tumor killing + homing peptide), only the homing peptide sequence is included in the database.