CLBTope Algorithm
Prediction of B-cell epitope not only aids immunologists in designing epitope based peptide vaccines but also promotes the development of accurate diagnostic kits and treatment
The prediction server for B-cell epitopes has been designed in a very user-friendly manner. Here, on this page, user can get the details of all the algorithms and procedures exploited in the different modules.
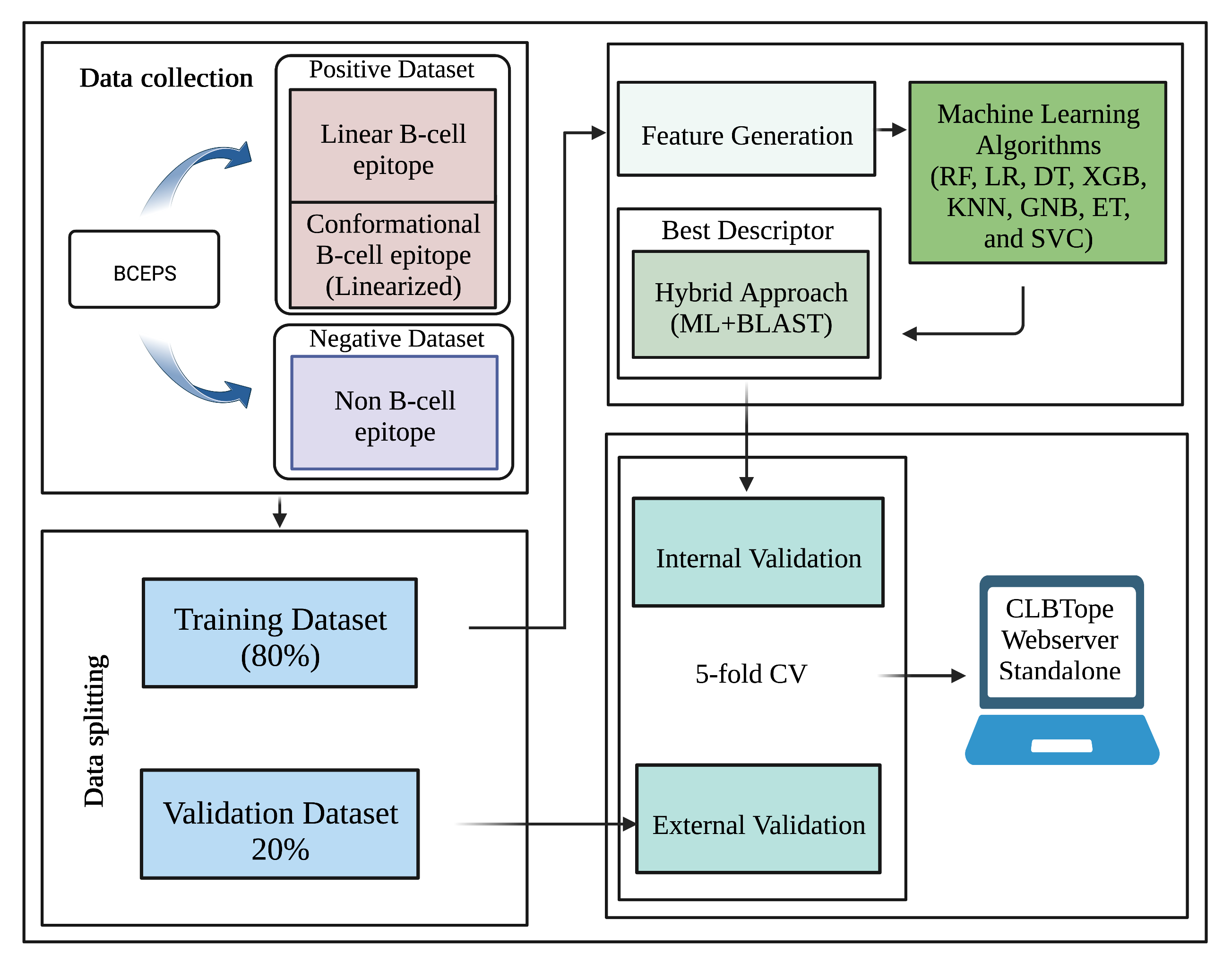
Dataset Used
Training Dataset
Dataset contains experimentally validated B-cell epitopes as positive peptides and non B-cell epitopes as negative peptides.
Validation Dataset
Dataset contains experimentally validated B-cell epitopes as positive peptides and non B-cell epitopes as negative peptides.
This algorithm of the server is relies on the following three models:
Prediction model
- This module allows users to predict the B-cell epitope in a set of peptides or peptide library (virtual screening). User may submit large number of peptides and server will predict and rank them based on their potential as B-cell epitopes or non B-cell epitope.
Design model
- It generate mutant of a query peptide and predict B-cell epitopes in mutants. This server allows users to identify minimum mutations required to increase its potency.
Scan model
- In this study, we incorporated three scan modules:
Protein Scan:
Aim of this approach is to identify B-cell epitopes regions in the protein sequence, which can futher removed or altered.Motif Scan:
Aim of this approach is to discover motifs or patterns in B-cell epitopes and non B-cell epitopes. In this study we used a powerful pattern discovery software MERCI. First we identified motifs are exclusively found in B-cell peptides and not present in non B-cell peptides. Similarly we identified motifs in non B-cell peptides which are absent in B-cell peptides. These novel motifs used for discriminating B-cell epitopes from non B-cell epitopes.Blast Scan:
“Blast Search” module is based on a similarity search method, i.e., Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST). The input query sequence is searched against the database of known B-cell peptides. A query sequence is predicted as B-cell epitope if found match or hit in the database; otherwise, it is predicted as non B-cell epitopes.