| ProGlyProt ID | BC172 |
| Organism Information |
| Organism Name | Pseudomonas syringae pv. tabaci 6605 |
| Domain | Bacteria |
| Classification | Family: Pseudomonadaceae
Order: Pseudomonadales
Class: Gammaproteobacteria
Division or phylum: "Proteobacteria" |
| Taxonomic ID (NCBI) | 322 |
| Genome Sequence (s) |
| EMBL | AB061230 |
| Gene Information |
| Gene Name | fliC |
| NCBI Gene ID | |
| Protein Information |
| Protein Name | Flagellin |
| UniProtKB/SwissProt ID | Q6I809 |
| NCBI RefSeq | |
| EMBL-CDS | BAD24670.1 |
| UniProtKB Sequence | >tr|Q6I809|Q6I809_PSESZ Flagellin OS=Pseudomonas syringae pv. tabaci GN=fliC PE=4 SV=1
MALTVNTNVASLNVQKNLGRASDALSTSMTRLSSGLKINSAKDDAAGLQIATKITSQIRG
QTMAIKNANDGMSLAQTAEGALQESTNILQRMRELAVQSRNDSNSSTDRDALNKEFTAMS
SELTRIAQSTNLNGKNLLDGSASTMTFQVGSNSGASNQITLTLSASFDANTLGVGSAVTI
AGSDSTTAETNFSAAIAAIDSALQTINSTRADLGAAQNRLTSTISNLQNINENASAALGR
VQDTDFAAETAQLTKQQTLQQASTSVLAQANQLPSAVLKLLQ
|
| Sequence length | 282 AA |
| Subcellular Location | Surface |
| Function | Flagellin, the major component of the flagella filament functions as one of the pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs). It is a major HR (hypersensitive reaction) elicitor in this pathogen but does not remarkably induce hypersensitive cell death in its host tobacco plants. |
| Protein Structure |
| PDB ID | |
| Glycosylation Status |
| Glycosylation Type | O (Ser) linked |
| Experimentally Validated Glycosite(s) in Full Length Protein | S143, S164, S176, S183, S193, S201 |
| Experimentally Validated Glycosite(s ) in Mature Protein | S143, S164, S176, S183, S193, S201 |
| Glycosite(s) Annotated Protein Sequence | >tr|Q6I809|Q6I809_PSESZ Flagellin OS=Pseudomonas syringae pv. tabaci GN=fliC PE=4 SV=1
MALTVNTNVASLNVQKNLGRASDALSTSMTRLSSGLKINSAKDDAAGLQIATKITSQIRG
QTMAIKNANDGMSLAQTAEGALQESTNILQRMRELAVQSRNDSNSSTDRDALNKEFTAMS
SELTRIAQSTNLNGKNLLDGSAS*(143)TMTFQVGSNSGASNQITLTLS*(164)ASFDANTLGVGS*(176) AVTI
AGS*(183)DSTTAETNFS*(193)AAIAAIDS*(201)ALQTINSTRADLGAAQNRLTSTISNLQNINENASAALGR
VQDTDFAAETAQLTKQQTLQQASTSVLAQANQLPSAVLKLLQ
|
| Sequence Around Glycosites (21 AA) | NGKNLLDGSASTMTFQVGSNS
GASNQITLTLSASFDANTLGV
SFDANTLGVGSAVTIAGSDST
GVGSAVTIAGSDSTTAETNFS
SDSTTAETNFSAAIAAIDSAL
NFSAAIAAIDSALQTINSTRA
|
| Glycosite Sequence Logo | seqlogo |
| Glycosite Sequence Logo | 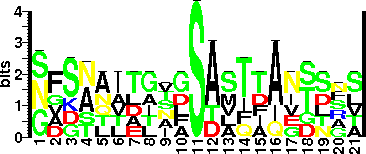 |
| Technique(s) used for Glycosylation Detection | Rapid migration on SDS-PAGE after chemical deglycosylation with TFMS, glycoprotein staining using GelCode® glycoprotein staining kit. |
| Technique(s) used for Glycosylated Residue(s) Detection | Site-directed mutagenesis and MALDI-TOF MS (matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization time of flight mass spectrometry) analysis |
| Protein Glycosylation- Implication | Glycosylation, especially at positions S176 and S183, is required for smooth motility and bacterial virulence. Glycosylation is one of the important process in bacterial HR-inducing (hypersensitive reaction, a rapid and strong plant defence response) activity. Glycosylation may also serve to mask elicitor function of flagellin molecule in order to avoid plant recognition. Glycosylation of sites that are most surface-exposed plays a role in the swarming motility of the P. syringae pv. tabaci 6605 |
| Glycan Information |
| Glycan Annotation | Linkage: α-L-Rha-Ser.
Tetrasaccharide, 4,6-dideoxy-4-(3-hydroxybutanamido)-2-O-methyl-Glcp-(1→3)-α-L-Rhap-(1→2)-α-L-Rhap-(1→2)-α-L-Rha-(1→, as well as a trisaccharide, 4,6-dideoxy-4-(3-hydroxybutanamido)-2-O-methyl-Glcp-(1→3)-α-L-Rhap-(1→2)-α-L-Rha-(1→. Rhamnose (Rha) is exclusively of the L form. 4,6-dideoxy-4-(3-hydroxy-3-methylbutanamido)-2-O-methylglucopyranose is named as viosamine. Therefore, in the glycans, modified viosamine is present.
The ratios of a tri |
| Technique(s) used for Glycan Identification | Sugar composition analysis using an ABEE (p-aminobenzoic acid ethyl ester) labeling kit, MALDI-TOF MS (matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization–time-of-flight mass spectrometry), determination of D-Rha/L-Rha ratios using gas chromatography (GC), and 1H-NMR analyses including 1H-1H correlation spectra [DQF-COSY (double quantum filtered correlation spectroscopy), TOCSY (total correlation spectroscopy), and NOESY (nuclear Overhauser and exchange spectroscopy)] and 1H-13C correlation spectra [H |
| Protein Glycosylation linked (PGL) gene(s) |
| OST Gene Name | |
| OST NCBI Gene ID | |
| OST GenBank Gene Sequence | |
| OST Protein Name | |
| OST UniProtKB/ SwissProt ID | |
| OST NCBI RefSeq | |
| OST EMBL-CDS | |
| OST UniProtKB Sequence | |
| OST EC Number (BRENDA) | |
| OST Genome Context | |
| Characterized Accessory Gene(s) | FGT1 and FGT2 are two glycosyltransferases which are encoded in the flagellin glycosylation island. Non-glycosylated and partially glycosylated flagellins were respectively produced by fgt1 and fgt2 mutants. |
| PGL Additional Links | CAZy |
| Literatures |
| Reference(s) | 1) Taguchi, F., Yamamoto, M., Ohnishi-Kameyama, M., Iwaki, M., Yoshida, M., Ishii, T., Konishi, T. and Ichinose, Y. (2010) Defects in flagellin glycosylation affect the virulence of Pseudomonas syringae pv. tabaci 6605. Microbiology, 156, 72-80. [PubMed: 19815579]
2) Konishi, T., Taguchi, F., Iwaki, M., Ohnishi-Kameyama, M., Yamamoto, M., Maeda, I., Nishida, Y., Ichinose, Y., Yoshida, M. and Ishii, T. (2009) Structural characterization of an O-linked tetrasaccharide from Pseudomonas syringa |
| Additional Comments | |
| Year of Identification | 2003 |
| Year of Validation | 2006 |


