| ProGlyProt ID | BC171 |
| Organism Information |
| Organism Name | Pseudomonas syringae pv. glycinea race 4 |
| Domain | Bacteria |
| Classification | Family: Pseudomonadaceae
Order: Pseudomonadales
Class: Gammaproteobacteria
Division or phylum: "Proteobacteria" |
| Taxonomic ID (NCBI) | 318 |
| Genome Sequence (s) |
| EMBL | AB061232 |
| Gene Information |
| Gene Name | fliC |
| NCBI Gene ID | |
| Protein Information |
| Protein Name | Flagellin |
| UniProtKB/SwissProt ID | Q76M64 |
| NCBI RefSeq | |
| EMBL-CDS | BAD06420.1 |
| UniProtKB Sequence | >tr|Q76M64|Q76M64_PSESG Flagellin OS=Pseudomonas syringae pv. glycinea GN=fliC PE=4 SV=1
MALTVNTNAASLNVQKNLGRASDALSTSMTRLSSGLKINSAKDDAAGLQIATKITSQIRG
QTMAIKNANDGMSLAQTAEGALQESTNILQRMRELAVQSRNDSNSSTDRDALNKEFTAMS
SELTRIAQSTNLNGKNLLDGSASTMTFQVGSNSGASNQITLTLSASFDANTLGVGSAVTI
AGSDSTTAETNFSAAIAAIDSALQTINSTRADLGAAQNRLTSTISNLQNINENASAALGR
VQDTDFAAETAQLTKQQTLQQASTSVLAQANQLPSAVLKLLQ |
| Sequence length | 282 AA |
| Subcellular Location | Surface |
| Function | Flagellin, the major component of the flagella filament functions as one of the pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs). It is able to induce hypersensitive cell death in its non-host tobacco plants. |
| Protein Structure |
| PDB ID | |
| Glycosylation Status |
| Glycosylation Type | O (Ser) linked |
| Experimentally Validated Glycosite(s) in Full Length Protein | S143, S164, S176, S183, S193, S201 |
| Experimentally Validated Glycosite(s ) in Mature Protein | S143, S164, S176, S183, S193, S201 |
| Glycosite(s) Annotated Protein Sequence | >tr|Q76M64|Q76M64_PSESG Flagellin OS=Pseudomonas syringae pv. glycinea GN=fliC PE=4 SV=1
MALTVNTNAASLNVQKNLGRASDALSTSMTRLSSGLKINSAKDDAAGLQIATKITSQIRG
QTMAIKNANDGMSLAQTAEGALQESTNILQRMRELAVQSRNDSNSSTDRDALNKEFTAMS
SELTRIAQSTNLNGKNLLDGSAS*(143)TMTFQVGSNSGASNQITLTLS*(164)ASFDANTLGVGS*(176)AVTI
AGS*(183)DSTTAETNFS*(193)AAIAAIDS*(201)ALQTINSTRADLGAAQNRLTSTISNLQNINENASAALGR
VQDTDFAAETAQLTKQQTLQQASTSVLAQANQLPSAVLKLLQ
|
| Sequence Around Glycosites (21 AA) | NGKNLLDGSASTMTFQVGSNS
GASNQITLTLSASFDANTLGV
SFDANTLGVGSAVTIAGSDST
GVGSAVTIAGSDSTTAETNFS
SDSTTAETNFSAAIAAIDSAL
NFSAAIAAIDSALQTINSTRA
|
| Glycosite Sequence Logo | seqlogo |
| Glycosite Sequence Logo | 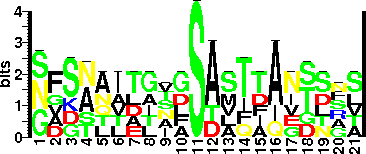 |
| Technique(s) used for Glycosylation Detection | Rapid migration on SDS-PAGE after chemical deglycosylation with TFMS, glycoprotein staining using GelCode® glycoprotein staining kit. |
| Technique(s) used for Glycosylated Residue(s) Detection | Site-directed mutagenesis and MALDI-TOF MS (matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization time of flight mass spectrometry) analysis |
| Protein Glycosylation- Implication | The flagellin glycan structures have a role to play in the virulence and host specificity of P. syringae. Glycosylation is important for the HR-inducing (hypersensitive reaction, a rapid and strong plant defence response) ability of the flagellin in plants. |
| Glycan Information |
| Glycan Annotation | Linkage: Rha-Ser.
S201 carries a unique trisaccharide consisting of two rhamnosyl (Rha) residues and one modified 4-amino-4,6-dideoxyglucosyl (Qui4N; named as viosamine) residue, ß-D-Quip4N(3-hydroxy-1-oxobutyl)2Me-(1→3)-α-L-Rhap-(1→2)-α-L-Rhap. The trisaccharide is present as the major glycan on each Ser residue. The glycans contain both L-Rha and D-Rha at a molar ratio of about 4:1.
Heterogeneity due to the addition of one or two units of mass value 147 is also observed. |
| Technique(s) used for Glycan Identification | Sugar composition analysis using an ABEE (p-aminobenzoic acid ethyl ester) labeling kit, MALDI-TOF MS (matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization–time-of-flight mass spectrometry), determination of D-Rha/L-Rha ratios using gas chromatography (GC), and 1H-NMR analyses including 1H-1H correlation spectra [DQF-COSY (double quantum filtered correlation spectroscopy), TOCSY (total correlation spectroscopy), and NOESY (nuclear Overhauser and exchange spectroscopy)] and 1H-13C correlation spectra [H |
| Protein Glycosylation linked (PGL) gene(s) |
| OST Gene Name | |
| OST NCBI Gene ID | |
| OST GenBank Gene Sequence | |
| OST Protein Name | |
| OST UniProtKB/ SwissProt ID | |
| OST NCBI RefSeq | |
| OST EMBL-CDS | |
| OST UniProtKB Sequence | |
| OST EC Number (BRENDA) | |
| OST Genome Context | |
| Characterized Accessory Gene(s) | Orf1 and Orf2 are putative glycosyltransferases encoded in the flagellin glycosylation island. |
| PGL Additional Links | CAZy |
| Literatures |
| Reference(s) | 1) Takeuchi, K., Ono, H., Yoshida, M., Ishii, T., Katoh, E., Taguchi, F., Miki, R., Murata, K., Kaku, H. and Ichinose, Y. (2007) Flagellin glycans from two pathovars of Pseudomonas syringae contain rhamnose in D and L configurations in different ratios and modified 4-amino-4,6-dideoxyglucose. J Bacteriol, 189, 6945-6956. [PubMed: 17644592]
2) Taguchi, F., Takeuchi, K., Katoh, E., Murata, K., Suzuki, T., Marutani, M., Kawasaki, T., Eguchi, M., Katoh, S., Kaku, H. et al. (2006) Identification |
| Additional Comments | |
| Year of Identification | 2003 |
| Year of Validation | 2006 |


