| ProGlyProt ID | BC169 |
| Organism Information |
| Organism Name | Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 |
| Domain | Bacteria |
| Classification | Family: Pseudomonadaceae
Order: Pseudomonadales
Class: Gammaproteobacteria
Division or phylum: "Proteobacteria" |
| Taxonomic ID (NCBI) | 287 |
| Genome Sequence (s) |
| GeneBank | AE004091.2 |
| EMBL | AE004091 |
| Gene Information |
| Gene Name | lecB (PA3361) |
| NCBI Gene ID | 882528 |
| GenBank Gene Sequence | 882528 |
| Protein Information |
| Protein Name | Lectin LecB (PA-IIL is old name) |
| UniProtKB/SwissProt ID | Q9HYN5 |
| NCBI RefSeq | NP_252051.1 |
| EMBL-CDS | AAG06749.1 |
| UniProtKB Sequence | >tr|Q9HYN5|Q9HYN5_PSEAE Fucose-binding lectin PA-IIL OS=Pseudomonas aeruginosa GN=lecB PE=1 SV=1
MATQGVFTLPANTRFGVTAFANSSGTQTVNVLVNNETAATFSGQSTNNAVIGTQVLNSGS
SGKVQVQVSVNGRPSDLVSAQVILTNELNFALVGSEDGTDNDYNDAVVVINWPLG |
| Sequence length | 115 AA |
| Subcellular Location | Periplasm or outer membrane |
| Function | LecB is a fucose-/mannose-specific lectin. It may help in the adhesion of P. aeruginosa cells to the receptors and facilitate biofilm formation resulting in host tissue colonization. This virulence factor has an important role in human infection. It inhibits the ciliary beating and hence defence mechanism of the lung. It is involved in cystic fibrosis. |
| Protein Structure |
| PDB ID | |
| Glycosylation Status |
| Glycosylation Type | N (Asn) linked |
| Experimentally Validated Glycosite(s) in Full Length Protein | N22 |
| Experimentally Validated Glycosite(s ) in Mature Protein | N22 |
| Glycosite(s) Annotated Protein Sequence | >tr|Q9HYN5|Q9HYN5_PSEAE Fucose-binding lectin PA-IIL OS=Pseudomonas aeruginosa GN=lecB PE=1 SV=1
MATQGVFTLPANTRFGVTAFAN*(22)SSGTQTVNVLVNNETAATFSGQSTNNAVIGTQVLNSGS
SGKVQVQVSVNGRPSDLVSAQVILTNELNFALVGSEDGTDNDYNDAVVVINWPLG
|
| Sequence Around Glycosites (21 AA) | NTRFGVTAFANSSGTQTVNVL |
| Glycosite Sequence Logo | seqlogo |
| Glycosite Sequence Logo | 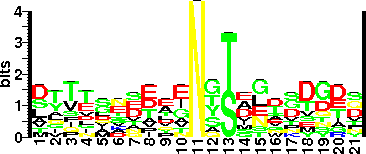 |
| Technique(s) used for Glycosylation Detection | Deglycosylation with N-glycosidase F (PNGase F) |
| Technique(s) used for Glycosylated Residue(s) Detection | Site-directed mutagenesis (N22A) |
| Protein Glycosylation- Implication | LecB N glycosylation seems to be important for its production and transport to the outer membrane. |
| Glycan Information |
| Glycan Annotation | |
| Technique(s) used for Glycan Identification | |
| Protein Glycosylation linked (PGL) gene(s) |
| OST Gene Name | |
| OST NCBI Gene ID | |
| OST GenBank Gene Sequence | |
| OST Protein Name | |
| OST UniProtKB/ SwissProt ID | |
| OST NCBI RefSeq | |
| OST EMBL-CDS | |
| OST UniProtKB Sequence | |
| OST EC Number (BRENDA) | |
| OST Genome Context | |
| Characterized Accessory Gene(s) | |
| PGL Additional Links | CAZy |
| Literatures |
| Reference(s) | 1) Bartels, K.M., Funken, H., Knapp, A., Brocker, M., Bott, M., Wilhelm, S., Jaeger, K.E. and Rosenau, F. (2011) Glycosylation is required for outer membrane localization of the lectin LecB in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol, 193, 1107-1113. [PubMed: 21217000] |
| Additional Comments | A LecB-deï¬cient P. aeruginosa strain has been shown to be impaired in bioï¬lm formation. |
| Year of Identification | 2011 |
| Year of Validation | 2011 |


