| ProGlyProt ID | BC160 |
| Organism Information |
| Organism Name | Paenibacillus (Bacillus) macerans and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens (velezensis) |
| Domain | Bacteria |
| Classification | Family: Bacillaceae
Order: Bacillales
Class: Bacilli (or Firmibacteria)
Division or phylum: "Firmicutes" |
| Taxonomic ID (NCBI) | 44252 |
| Genome Sequence (s) |
| EMBL | X55959 |
| Gene Information |
| Gene Name | |
| NCBI Gene ID | |
| Protein Information |
| Protein Name | H(A16-M) (1,3-1,4)-beta-glucanase |
| UniProtKB/SwissProt ID | P23904 |
| NCBI RefSeq | |
| EMBL-CDS | CAA39426.1 |
| UniProtKB Sequence | >sp|P23904|GUB_PAEMA Beta-glucanase OS=Paenibacillus macerans PE=1 SV=2
MKKKSCFTLVTTFAFSLIFSVSALAGSVFWEPLSYFNRSTWEKADGYSNGGVFNCTWRAN
NVNFTNDGKLKLGLTSSAYNKFDCAEYRSTNIYGYGLYEVSMKPAKNTGIVSSFFTYTGP
AHGTQWDEIDIEFLGKDTTKVQFNYYTNGVGGHEKVISLGFDASKGFHTYAFDWQPGYIK
WYVDGVLKHTATANIPSTPGKIMMNLWNGTGVDDWLGSYNGANPLYAEYDWVKYTSN |
| Sequence length | 237 AA |
| Subcellular Location | Secreted |
| Function | It is the hybrid enzyme that catalyses cleavage of (1,4)-beta-linkages of O-substituted beta-D-glucanopyranosyl residues. |
| Protein Structure |
| PDB ID | 1CPM, 1GLH |
| Glycosylation Status |
| Glycosylation Type | N (Asn) linked |
| Experimentally Validated Glycosite(s) in Full Length Protein | (Signal peptide: 1-23) N54, N208 |
| Experimentally Validated Glycosite(s ) in Mature Protein | N31, N185 |
| Glycosite(s) Annotated Protein Sequence | MKKKSCFTLVTTFAFSLIFSVSALAQTGGSFFEPFNSYNSGTWEKADGYSNGGVFN*(56)CTWR
ANNVNFTNDGKLKLGLTSSAYNKFDCAEYRSTNIYGYGLYEVSMKPAKNTGIVSSFFTYT
GPAHGTQWDEIDIEFLGKDTTKVQFNYYTNGVGGHEKVISLGFDASKGFHTYAFDWQPGY
IKWYVDGVLKHTATANIPSTPGKIMMNLWN*(210)GTGVDDWLGSYNGANPLYAEYDWVKYTSN
This sequence has 16 N-terminal amino acids (colored dark-green) derived from AMY. The remaining residues are from MAC. |
| Sequence Around Glycosites (21 AA) | ADGYSNGGVFNCTWRANNVNF
TPGKIMMNLWNGTGVDDWLGS
|
| Glycosite Sequence Logo | seqlogo |
| Glycosite Sequence Logo | 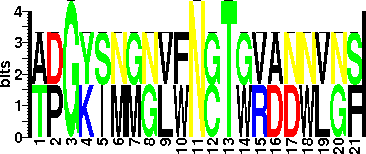 |
| Technique(s) used for Glycosylation Detection | Mass shift detected after deglycosylation with Endo Hf and PNGase F |
| Technique(s) used for Glycosylated Residue(s) Detection | N-terminal sequencing |
| Protein Glycosylation- Implication | There is a large influence of N glycosylation on the thermostability of the hybrid enzyme. 16- and 133-fold decrease of thermostability has been observed after treatment with endoglycosidase H and peptide:N-glycosidase F (that remove glycans). This indicates that N-glycans are a major determinant for the resistance of this hybrid glucanase to thermal inactivation. |
| Glycan Information |
| Glycan Annotation | |
| Technique(s) used for Glycan Identification | |
| Protein Glycosylation linked (PGL) gene(s) |
| OST Gene Name | |
| OST NCBI Gene ID | |
| OST GenBank Gene Sequence | |
| OST Protein Name | |
| OST UniProtKB/ SwissProt ID | |
| OST NCBI RefSeq | |
| OST EMBL-CDS | |
| OST UniProtKB Sequence | |
| OST EC Number (BRENDA) | |
| OST Genome Context | |
| Characterized Accessory Gene(s) | |
| PGL Additional Links | CAZy |
| Literatures |
| Reference(s) | 1) Hahn, M., Keitel, T. and Heinemann, U. (1995) Crystal and molecular structure at 0.16-nm resolution of the hybrid Bacillus endo-1,3-1,4-beta-D-glucan 4-glucanohydrolase H(A16-M). Eur J Biochem, 232, 849-858. [PubMed: 7588726]
2) Hahn, M., Piotukh, K., Borriss, R. and Heinemann, U. (1994) Native-like in vivo folding of a circularly permuted jellyroll protein shown by crystal structure analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 91, 10417-10421. [PubMed: 7937966]
3) Keitel, T., Meldgaard, M. |
| Additional Comments | Engineered glycoprotein
The glucanases from which the hybrid enzyme is made, are not glycosylated in their native hosts. Hybrid enzyme containing 16 N-terminal amino acids from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens (1,3-1,4)-beta-glucanase (AMY), and remaining C-terminal part and signal peptide from B. macerans (1,3-1,4)-beta-glucanase (MAC), was expressed in Saccharomyces cerevisiae to see the effect of N-glycosylation on the thermostability of the hybrid enzyme.
Information from UniProtKB and E |
| Year of Identification | 1994 |
| Year of Validation | 1994 |


