| ProGlyProt ID | BC155 |
| Organism Information |
| Organism Name | Neisseria gonorrhoeae N400 /MS11 |
| Domain | Bacteria |
| Classification | Family: Neisseriaceae
Order: Neisseriales
Class: Betaproteobacteria
Division or phylum: "Proteobacteria" |
| Taxonomic ID (NCBI) | 485 |
| Genome Sequence (s) |
| EMBL | K02078 |
| Gene Information |
| Gene Name | pilE1 |
| NCBI Gene ID | |
| Protein Information |
| Protein Name | Fimbrial protein (pilin) |
| UniProtKB/SwissProt ID | P02974 |
| NCBI RefSeq | |
| EMBL-CDS | AAA25466.1 |
| UniProtKB Sequence | >sp|P02974|FMM1_NEIGO Fimbrial protein OS=Neisseria gonorrhoeae GN=pilE1 PE=1 SV=2
MNTLQKGFTLIELMIVIAIVGILAAVALPAYQDYTARAQVSEAILLAEGQKSAVTEYYLN
HGKWPENNTSAGVASPPSDIKGKYVKEVEVKNGVVTATMLSSGVNNEIKGKKLSLWARRE
NGSVKWFCGQPVTRTDDDTVADAKDGKEIDTKHLPSTCRDNFDAK
|
| Sequence length | 165 AA |
| Subcellular Location | Surface |
| Function | Major pilin subunit protein of the type IV pilus (Tfp) colonization factor. Type IV pili (Tfp) are proteinaceous polymeric filaments that serve critical roles in disease pathogenesis and prokaryotic cell biology in many Gram-negative species. These multifunctional virulence factors are involved in adhesion to host cell surfaces, modulation of target cell specificity, twitching motility, bacteriophage adsorption and pilus retraction.
|
| Protein Structure |
| PDB ID | 2HI2, 2HIL |
| Glycosylation Status |
| Glycosylation Type | O (Ser) linked |
| Experimentally Validated Glycosite(s) in Full Length Protein | (Propeptide: 1-7) S70
|
| Experimentally Validated Glycosite(s ) in Mature Protein | S63
|
| Glycosite(s) Annotated Protein Sequence | >sp|P02974|FMM1_NEIGO Fimbrial protein OS=Neisseria gonorrhoeae GN=pilE1 PE=1 SV=2
MNTLQKGFTLIELMIVIAIVGILAAVALPAYQDYTARAQVSEAILLAEGQKSAVTEYYLN
HGKWPENNTS*(70)AGVASPPSDIKGKYVKEVEVKNGVVTATMLSSGVNNEIKGKKLSLWARRE
NGSVKWFCGQPVTRTDDDTVADAKDGKEIDTKHLPSTCRDNFDAK
|
| Sequence Around Glycosites (21 AA) | NHGKWPENNTSAGVASPPSDI |
| Glycosite Sequence Logo | seqlogo |
| Glycosite Sequence Logo | 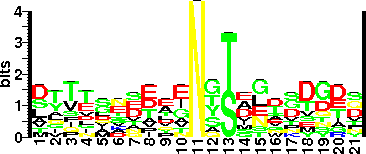 |
| Technique(s) used for Glycosylation Detection | Crystallographic analysis (electron density maps) |
| Technique(s) used for Glycosylated Residue(s) Detection | Crystallographic analysis (electron density maps) |
| Protein Glycosylation- Implication | Recently, using primary, human, cervical epithelial (i.e. pex) cells, pilin glycan has been shown to mediate productive cervical infection. For the first time, direct role of the protein-associated bacterial glycan in pathogenesis has been demonstrated (Ref. no. 1). Pilin glycan helps gonococci in binding to the compliment receptor 3 (CR3) I-domain expressed by pex cells when it is in a closed, low-affinity conformation. This leads to the acive state of CR3. |
| Glycan Information |
| Glycan Annotation | Linkage: Bac/DATDH-Ser.
Disaccharide composed of a hexose residue linked to a proximal 2,4-diacetamido-2,4,6-trideoxyhexose sugar (HexDATDH). Various X-ray diffraction studies have identified α-D-galactopyranosyl-(1→3)-2,4-diacetamido-2,4-dideoxy-β-D-glucopyranoside (bacillosamine, Bac); Gal-DADDGlc; and GlcNAc-α1,3-Gal, as glycans. DADDGlc has a second acetamido group at C4 of the proximal glucose in place of the hydroxyl group. DADDGlc thus resembles DATDH. However, DATDH lacks the C |
| Technique(s) used for Glycan Identification | Crystallographic analysis (electron density maps) and mass spectrometry (MS/MS) |
| Protein Glycosylation linked (PGL) gene(s) |
| OST Gene Name | pglO |
| OST NCBI Gene ID | 3282309 |
| OST GenBank Gene Sequence | 3282309 |
| OST Protein Name | PglO |
| OST UniProtKB/ SwissProt ID | Q5FAE1 |
| OST NCBI RefSeq | YP_207258.1 |
| OST EMBL-CDS | AAW88846.1 |
| OST UniProtKB Sequence | >tr|Q5FAE1|Q5FAE1_NEIG1 Pilin glycosylation protein OS=Neisseria gonorrhoeae (strain ATCC 700825 / FA 1090) GN=NGO0085 PE=4 SV=1
MSKAVKRLFDIIASASGLIVLSPVFLVLIYLIRKNLGSPVFFIRERPGKDGKPFKMVKFR
SMRDALDSDGIPLPDSERLTDFGKKLRATSLDELPELWNVLKGEMSLVGPRPLLMQYLPL
YNKFQNRRHEMKPGITGWAQVNGRNALSWDEKFSCDVWYTDNFSFWLDMKILFLTVKKVL
IKEGISAQGEATMPPFAGNRKLAVIGAGGHGKVVAELAAALGTYGEIVFLDDRTQGSVNG
FPVIGTTLLLENSLSPEQFDITVAVGNNRIRRQITENAAALGFKLPVLIHPDATVSPSAI
IGQGSVVMAKAVVQAGSVLKDGVIVNTAATVDHDCLLDAFVHISPGAHLSGNTRIGEESR
IGTGACSRQQTTVGSGVTAGAGAVIVCDIPDGMTVAGNPAKPLTGKNPKTGTA
|
| OST EC Number (BRENDA) | |
| OST Genome Context | Q5FAE1 |
| Characterized Accessory Gene(s) | PglA, PglB2, PglE. Galactosyltransferase PglA transfers the galactose to DATDH. PglE catalyzes the attachment of the terminal galactose to the glycan. PglBCD enzymes are essential for biosynthesis of DATDH from GlcNAc. PglB (B1) also catalyzes transfer of DATDH onto the lipid carrier. PglF is the flippase. PglB2 is a glyceramido transferase that synthesizes GATDH and transfers it onto the lipid carrier. PglE has a relaxed substrate specificity. In the majority of the gonococcal strains, PglE is switched off. |
| PGL Additional Links | CAZy |
| Literatures |
| Reference(s) | 1) Jennings, M.P., Jen, F.E., Roddam, L.F., Apicella, M.A. and Edwards, J.L. (2011) Neisseria gonorrhoeae pilin glycan contributes to CR3 activation during challenge of primary cervical epithelial cells. Cell Microbiol, 13, 885-896. [PubMed: 21371235]
2) Aas, F.E., Vik, A., Vedde, J., Koomey, M. and Egge-Jacobsen, W. (2007) Neisseria gonorrhoeae O-linked pilin glycosylation: functional analyses define both the biosynthetic pathway and glycan structure. Mol Microbiol, 65, 607-624. [PubMed: 1 |
| Additional Comments | Replacing the pglB1 allele with the pglB2 allele from the N. meningitidis 8013 strain results in the synthesis of glycan with GATDH (2-acetamido 4-glyceramido 2,4,6-trideoxyhexose).
Glycan formation is phase variable.
Sequon feature: S/T plus low complexity region, the glycan modiï¬cations are found on a flexible-loop region within the globular domain of the protein. |
| Year of Identification | 1995 |
| Year of Validation | 1995 |


