| ProGlyProt ID | AC108 |
| Organism Information |
| Organism Name | Haloferax volcanii DS2 |
| Domain | Archaea |
| Classification | Family: Halobacteriaceae
Order: Halobacteriales
Class: Halobacteria or Halomebacteria
Division or phylum: "Euryarchaeota" |
| Taxonomic ID (NCBI) | 2246 |
| Genome Sequence (s) |
| GeneBank | CP001956.1 |
| EMBL | M62816 |
| Gene Information |
| Gene Name | csg |
| NCBI Gene ID | 8924493 |
| GenBank Gene Sequence | 8924493 |
| Protein Information |
| Protein Name | S-lyer glycoprotein |
| UniProtKB/SwissProt ID | P25062 |
| NCBI RefSeq | YP_003536097.1 |
| EMBL-CDS | AAA72996.1 |
| UniProtKB Sequence | >sp|P25062|CSG_HALVO Cell surface glycoprotein OS=Halobacterium volcanii GN=csg PE=1 SV=1
MTKLKDQTRAILLATLMVTSVFAGAIAFTGSAAAERGNLDADSESFNKTIQSGDRVFLGE
EISTDAGLGASNPLLTGTAGNSEGVSLDLSSPIPQTTENQPLGTYDVDGSGSATTPNVTL
LAPRITDSEILTSSGGDVTGSAISSSDAGNLYVNADYNYESAEKVEVTVEDPSGTDITNE
VLSGTDTFVDDGSIGSTSSTGGGVGIDMSDQDAGEYTIILEGAEDLDFGDATETMTLTIS
SQDEIGIELDSESVTQGTDVQYTVTNGIDGNEHVVAMDLSDLQNDATTEQAKEVFRNIGD
TSEVGIANSSATNTSGSSTGPTVETADIAYAVVEIDGASAVGGIETQYLDDSEVDLEVYD
AGVSATAAVGQDATNDITLTIEEGGTTLSSPTGQYVVGSEVDINGTATSSDSVAIYVRDD
GDWQLLEIGGDNEISVDSDDTFEEEDIALSGLSGDGSSILSLTGTYRIGVIDASDADVGG
DGSVDDSLTTSEFTSGVSSSNSIRVTDQALTGQFTTINGQVAPVETGTVDINGTASGANS
VLVIFVDERGNVNYQEVSVDSDGTYDEDDITVGLTQGRVTAHILSVGRDSAIGDGSLPSG
PSNGATLNDLTGYLDTLDQNNNNGEQINELIASETVDETASDDLIVTETFRLAESSTSID
SIYPDAAEAAGINPVATGETMVIAGSTNLKPDDNTISIEVTNEDGTSVALEDTDEWNNDG
QWMVEIDTTDFETGTFTVEADDGDNTDTVNVEVVSEREDTTTSSDNATDTTTTTDGPTET
TTTAEPTETTEEPTEETTTSSNTPGFGIAVALVALVGAALLALRREN
|
| Sequence length | 827 AA |
| Subcellular Location | Surface |
| Function | In Archaea, which do not possess other cell wall components, the S-layer has to maintain the cell integrity and stabilize as well as to protect the cell against mechanical and osmotic stresses or extreme pH conditions. It is also predicted that the S-layer has to maintain or even determine the cell shape.
|
| Protein Structure |
| PDB ID | |
| Glycosylation Status |
| Glycosylation Type | N (Asn) linked, (O, Thr-linked residues not known) |
| Experimentally Validated Glycosite(s) in Full Length Protein | (Signal peptide: 1-34) N47, N117, N308, N313, N532
|
| Experimentally Validated Glycosite(s ) in Mature Protein | N13, N83, N274, N279, N498
|
| Glycosite(s) Annotated Protein Sequence | >sp|P25062|CSG_HALVO Cell surface glycoprotein OS=Halobacterium volcanii GN=csg PE=1 SV=1
MTKLKDQTRAILLATLMVTSVFAGAIAFTGSAAAERGNLDADSESFN*(47)KTIQSGDRVFLGE
EISTDAGLGASNPLLTGTAGNSEGVSLDLSSPIPQTTENQPLGTYDVDGSGSATTPN*(117)VTL
LAPRITDSEILTSSGGDVTGSAISSSDAGNLYVNADYNYESAEKVEVTVEDPSGTDITNE
VLSGTDTFVDDGSIGSTSSTGGGVGIDMSDQDAGEYTIILEGAEDLDFGDATETMTLTIS
SQDEIGIELDSESVTQGTDVQYTVTNGIDGNEHVVAMDLSDLQNDATTEQAKEVFRNIGD
TSEVGIAN*(308)SSATN*(313)TSGSSTGPTVETADIAYAVVEIDGASAVGGIETQYLDDSEVDLEVYD
AGVSATAAVGQDATNDITLTIEEGGTTLSSPTGQYVVGSEVDINGTATSSDSVAIYVRDD
GDWQLLEIGGDNEISVDSDDTFEEEDIALSGLSGDGSSILSLTGTYRIGVIDASDADVGG
DGSVDDSLTTSEFTSGVSSSNSIRVTDQALTGQFTTINGQVAPVETGTVDIN*(532)GTASGANS
VLVIFVDERGNVNYQEVSVDSDGTYDEDDITVGLTQGRVTAHILSVGRDSAIGDGSLPSG
PSNGATLNDLTGYLDTLDQNNNNGEQINELIASETVDETASDDLIVTETFRLAESSTSID
SIYPDAAEAAGINPVATGETMVIAGSTNLKPDDNTISIEVTNEDGTSVALEDTDEWNNDG
QWMVEIDTTDFETGTFTVEADDGDNTDTVNVEVVSEREDTTTSSDNATDTTTTTDGPTET
TTTAEPTETTEEPTEETTTSSNTPGFGIAVALVALVGAALLALRREN
|
| Sequence Around Glycosites (21 AA) | GNLDADSESFNKTIQSGDRVF
VDGSGSATTPNVTLLAPRITD
IGDTSEVGIANSSATNTSGSS
EVGIANSSATNTSGSSTGPTV
APVETGTVDINGTASGANSVL
|
| Glycosite Sequence Logo | seqlogo |
| Glycosite Sequence Logo | 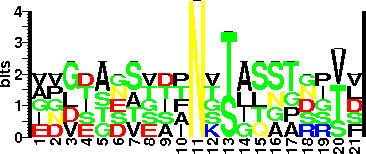 |
| Technique(s) used for Glycosylation Detection | Deglycosylation with anhydrous hydrogen fluoride. |
| Technique(s) used for Glycosylated Residue(s) Detection | Nano-LC-ES-MS/MS (nano-liquid chromatography-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry) |
| Protein Glycosylation- Implication | N-glycosylation endows H. volcanii with an ability to maintain an intact and stable cell envelope (correct S-layer architecture and stable association of the S-layer glycoprotein within the S-layer) in hypersaline surroundings, ensuring survival in this extreme environment. |
| Glycan Information |
| Glycan Annotation | Linkage: βGlc-Asn, Gal-Thr.
N glycosylated with a Pentasaccharide (2 hexoses, 2 hexuronic acids and a methyl ester of hexuronic acid). Pentasaccharide sequence is: hexose (Hex)-X-hexuronic acid (HexA)-HexA-Hex-peptide, where X is a 190 Da moiety, likely to be either dimethylated hexose or the methyl ester of hexuronic acid. Relatively minor amount of the completed pentasaccharide as compared to the level of tetrasaccharide as well as Di- and trisaccharide-bearing species were detected duri |
| Technique(s) used for Glycan Identification | |
| Protein Glycosylation linked (PGL) gene(s) |
| OST Gene Name | aglB |
| OST NCBI Gene ID | 8923906 |
| OST GenBank Gene Sequence | 8923906 |
| OST Protein Name | AglB |
| OST UniProtKB/ SwissProt ID | D4GYH4 |
| OST NCBI RefSeq | YP_003535577.1 |
| OST EMBL-CDS | ADE03209.1 |
| OST UniProtKB Sequence | >tr|D4GYH4|D4GYH4_HALVD Oligosaccharyltransferase AglB OS=Haloferax volcanii (strain ATCC 29605 / DSM 3757 / IFO 14742 / NCIMB 2012 / DS2) GN=aglB PE=4 SV=1
MSDEQTKYSPSIAELARDWYHIPVLSTIILVMLWIRLRSYDAFIREGTVFFSGNDAWYHL
RQVEYTVRNWPATMPFDPWTEFPFGRTAGQFGTIYDQLVATAALVVGLGSPSSDLVAKSL
LVAPAVFGALTVIPTYLIGKRLGGRLGGLFGAVILMLLPGTFLQRGLVGFADHNIVEPFF
MGFAVLAIMIALTVADREKPVWELVAARDLDALREPLKWSVLAGVATAIYMWSWPPGILL
VGIFGLFLVLKMASDYVRGRSPEHTAFVGAISMTVTGLLMFIPIEEPGFGVTDFGFLQPL
FSLGVALGAVFLAALARWWESNDVDERYYPAVVGGTMLVGIVLFSLVLPSVFDSIARNFL
RTVGFSAGAATRTISEAQPFLAANVLQSNGQTAVGRIMSEYGFTFFTGALAAVWLVAKPL
VKGGNSRKIGYAVGSLALIGVLFLIPALPAGIGSALGVEPSLVSLTIVTALIVGAVMQAD
YESERLFVLVWAAIITSAAFTQVRFNYYLAVVVAVMNAYLLREALGIDFVGLANVERFDD
ISYGQVAAVVIAVLLILTPVLIIPIQLGNGGVSQTAMQASQTGPGTVTQWDGSLTWMQNN
TPAEGEFGGESNRMEYYGTYEYTDDFDYPDGAYGVMSWWDYGHWITVLGERIPNANPFQG
GATEAANYLLAEDEQQAESVLTSMGDDGEGDQTRYVMVDWQMASTDAKFSAPTVFYDESN
ISRSDFYNPMFRLQEQGEQTTVAAASSLKDQRYYESLMVRLYAYHGSAREASPIVVDWEE
RTSADGSTTFRVTPSDGQAVRTFDNMSAAEEYVANDPTSQIGGIGTFPEE |
| OST EC Number (BRENDA) | 2.4.1.119 |
| OST Genome Context | |
| Characterized Accessory Gene(s) | AglD, AglE, AglI, AglG and AglJ are glycosyltransferases involved in the pentasaccharide assembly. AglJ adds the first sugar of the glycan and AglD adds the last one. All except AglD are encoded in the agl gene island or cluster. aglB is also present in this island.
Characterized by a combination of gene deletion, Mass spectroscopy and biochemical characterization |
| PGL Additional Links | CAZy |
| Literatures |
| Reference(s) | 1) Kaminski, L., Abu-Qarn, M., Guan, Z., Naparstek, S., Ventura, V.V., Raetz, C.R., Hitchen, P.G., Dell, A. and Eichler, J. (2010) AglJ adds the first sugar of the N-linked pentasaccharide decorating the Haloferax volcanii S-layer glycoprotein. J Bacteriol, 192, 5572-5579. [PubMed: 20802039]
2) Kaminski, L. and Eichler, J. (2010) Identification of residues important for the activity of Haloferax volcanii AglD, a component of the archaeal N-glycosylation pathway. Archaea, 2010, 315108. [PubM |
| Additional Comments | Based on analogy to H. salinarium and presence of similar glycans, the S layer protein in H. volcanni that exhibits a cluster of threonine residues (yet uncharacterized) at C terminus of the protein nearby hydrophobic membrane anchor has been speculated to be glycosylated with glucosyl-(1-2)-galactose disaccharides. The probable glycosylated cluster sequence has been attributed to act as a spacer between membrane anchor and extracellular domain akin to periplasmic space in gram negative bacteria |
| Year of Identification | 1990 |
| Year of Validation | 1992 |


