Conformation
Conformational isomerism is a form of isomerism that describes the phenomenon of molecules with the same structural formula having different shapes due to rotations about one or more bonds. Different conformations might have different energies, can usually interconvert, and are very rarely isolatable.
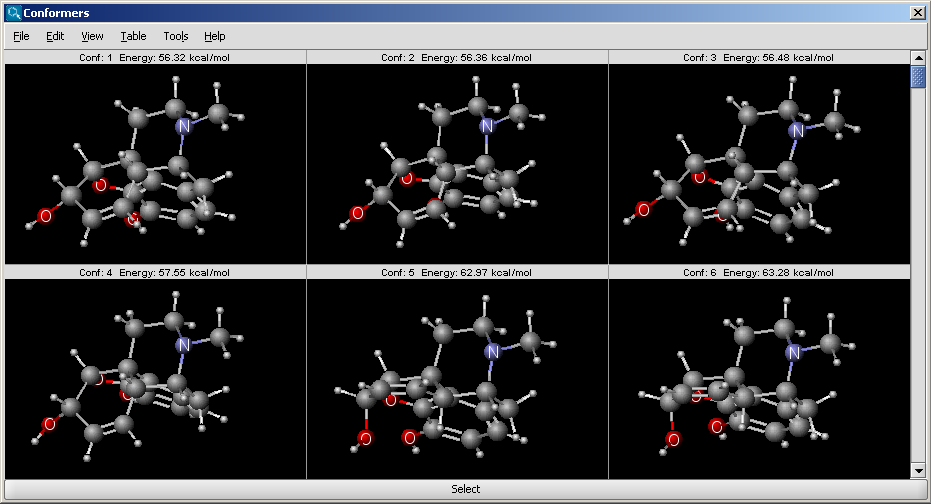
Conformer plugin generates selected number of conformers or
the lowest energy conformer of a molecule. For conformer calculation
Dreiding force field is used.
Different calculation parameters can be set in the Conformers Options panel:
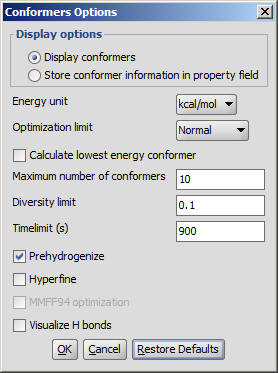 |
- Display options
- Display conformers: conformers are displayed in a MarivnView window.
- Store conformer information in property field: the conformer data are calculated and stored with the structures. This option provides the calculations needed to select a specific conformer when using 3D cleaning (menu item Structure > Clean 3D > Display Stored Conformers). The conformers will only be stored if you select one result and click on "Select".
- Energy unit: giving results in kcal/mol or kJ/mol.
-
Optimization limit: set the optimization to loose, normal, strict very strict (in this order increasing calculation times and precisity).
-
Calculate lowest energy conformer: calculates and displays only the lowest energy conformer structure. When checking this option, max. number if conformers and diversity limit are disabled.
-
Maximum numbers of conformers: limiting the number of calculated structures.
-
Diversity limit: conformers within diversity limit will be considered the same and doubles removed.
-
Timelimit (s): no conformers will be displayed if the calculation is stopped at the time limit set (e.g. there are too many conformers to calculate, the operation is cancelled after the given time had elapsed).
-
Prehydrogenize: if checked, converts all implicit hydrogens to explicit hydrogens without removing them after the calculation. If unchecked, no explicit hydrogens will be added.
-
Hyperfine: inserts more itineration steps in the calculations, gives more precision in results but the needed time becomes longer.
-
MMFF94 optimization: applies MMFF94 optimization in the calculations.
-
Visualize H bonds: marks intramolecular hydrogen bonds in the conformer where it is likely to occur.
The results appear in a new window, containing all calculated conformers with their energy indicated:
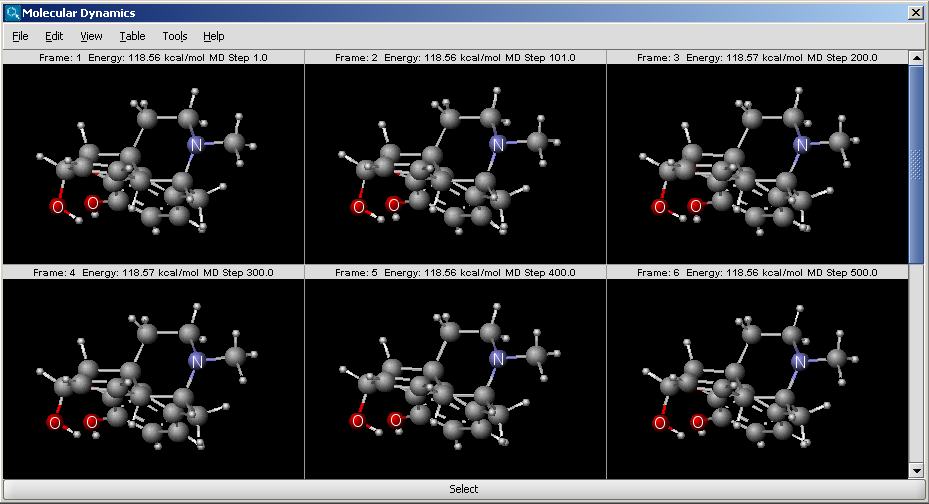
The molecular dynamics plugin calculates the configurations of
the system by integrating Newton's laws of motion.
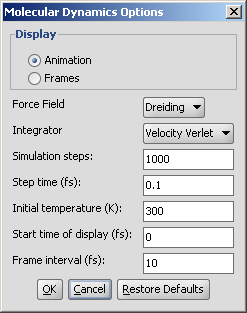
The calculation and the display options can be set in the Molecular Dynamics
Options panel:
- Display: display mode
- Animation: trajectory is displayed as an animation.
- Frames: trajectory frames are displayed individually (see above).
- Force field: force field used for calculation.
- Integrator: integrator type used for solving Newton's
laws of motion.
- Simulation steps: number of simulation steps.
- Step time (fs): time between simulation steps in femtoseconds.
- Initial temperature (K): initial temperature of the system
in kelvin.
- Start time of display (fs): the time of the first simulation
frame to be displayed in femtoseconds.
- Frame interval (fs): time between displayed simulation
frames in femtoseconds.
The result is shown in a new window:
The window is a MarvinView window, with all its funcionalities to reach.
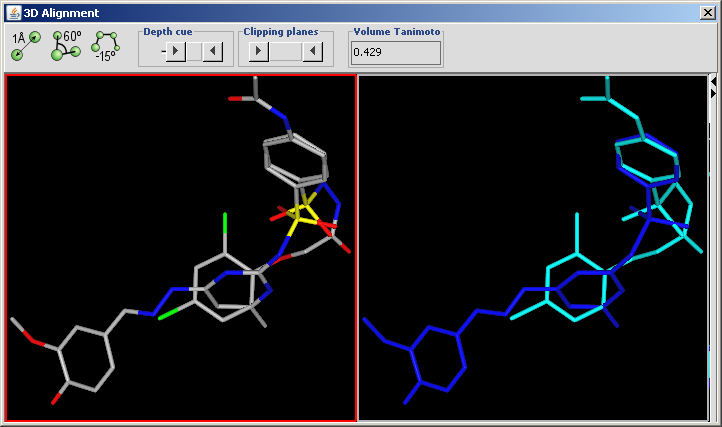
3D Alignment overlays drug sized molecules onto each other in the 3D space.
Input can be two or more molecules in 2D or in 3D. If 2D molecules are used their 3D structure is automatically generated by generate3D.
The conformation of the molecules can be treated flexible or the input conformation can be preserved. To preserve the input conformation simply select the molecule.
Usage: Molecules to align shoud be placed into the same MarvinSketch canvas by reading multiple molecules from a file. Alternatively, copy & paste or drag molecules from another sketch window.
Output is the aligned molecules in 3D. To save the aligned orientation use the popup menu: Click on the molecules with the second mouse button.
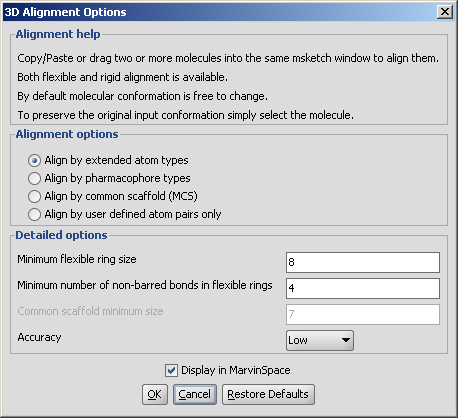
Following options can be set in the 3D Alignment
Options panel:
Alignment options
- Align by extended atom types: Extended atom types are assigned to each atom to enable chemically relevant atomic overlay. During the alignment process the overlap of the atoms of the same type is maximized. Types differentiate atomic number, hybridization state and aromaticity, e.g. aromatic nitrogen atom is not matched against a tertiary amine. These extended atom types correspond to the ones used in Dreiding force field.
- Align by pharmacophoric properties: Atoms are overlaid by their pharmacophoric properties: positive, negative, aromatic, hydrophobic, H bond donor and acceptor. Directionality is also taken into account at the H bonds. Atoms of the same types are attempted to align.
- Align by extended atom types: The atom-atom pairing is obtained from the 2D maximum common substructure of the molecules. Alignment by extended atom types is applied on the non MCS atoms.
- Align by user defined atom pairs: Atom pairings can be defined manually between molecules using the reaction arrow (Mapping atoms). These pairs will be considered to introduce user constraints into alignments above or can be used exclusively.
Detailed options
Conformation of rings or macrocycles can also be treated flexible if both of the following two criteria are fulfilled:
- Minimum flexible ring size: Rings are treated flexible in case their size (number of atoms) exceeds this limit.
- Minimum number of non-barred bonds in flexible rings: Rings are treated flexible in case their non barred bond count exceeds this limit. Barred bonds are aromatic, amide, double, a member of another ring that is not flexible and a single bond that connects two aromatic rings.
- Common scaffold minimum size: Only available at MCS based alignment. Minimum number of atoms that are required for the maximum common substructure calculation prior to the alignment.
- Accuracy: low, normal, high, very high: If lower selected the calcualtion is faster. The default is normal.
- Display in MarvinSpace: the result window is a MarvinSpace 3D viewer. Molecules are visualized in different colors for better distinction of structures.
The aligned molecules are shown in a MarvinSpace window. Click and drag to rotate.
An example of usage
Suppose you have an SDfile contaning some molecules (called wish.sdf) that you wish to align. This must be converted for the alignment to a single molecule multi-fragment file where each fragment is a molecule from wish.sdf:
- Create an empty file in MarvinSketch called empty.mol
- Type at command prompt:
molconvert mol empty.mol -R wish.sdf -o wish_fused.mol
- Open wish_fused.mol in MarvinSketch
If you know which atoms to overlap use the Reaction arrow tool to connect them. This can improve the alignment. If you have only 3D molecules as input and you select one of them, its original conformation will be preserved during the alignment, while others remain flexible.
- Select Tools > Conformation > 3D Alignment
- Untick the Display in MarvinSpace option
- Alignment process can take a while, around a minute for 4 drugsize molecules
- Click on the result window with the right mouse button and select "Save As" from the pop menu.